NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Conservation of Plants and Animals
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals includes all the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science in form of pdf, worksheet and free to download.
7. Conservation Of Plants And Animals
7.1 Deforestation and Its Causes
7.2 Consequences of Deforestation
7.3 Conservation of Forest and Wildlife
7.4 Biosphere Reserve
7.5 Flora and Fauna
7.6 Endemic Species
7.7 Wildlife Sanctuary
7.8 National Park
7.9 Red Data Book
7.10 Migration
7.11 Recycling of Paper
7.12 Reforestation
-------------------------------------------------------------
Board CBSE
-------------------------------------------------------------
TextBook NCERT
-------------------------------------------------------
CLASS Class 8
--------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Science
----------------------------------------------------------
CHAPTER Chapter 7
-------------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Conservation of Plants and Animals
--------------------------------------------------------------
Category NCERT Solutions
---------------------------------------------------------------
Keywords of the lesson NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals:
Biodiversity : Biodiversity is a term used to describe the enormous variety of life on Earth. It can be used more specifically to refer to all of the species in one region or ecosystem. Biodiversity refers to every living thing, including plants, bacteria, animals, and humans.
Biosphere Reserve : A Biosphere Reserve is a large protected area of land meant for the conservation of wildlife, biodiversity, and the traditional lifestyle of the tribal people living in the area. In creating the large areas of conservation called Biosphere Reserves. Biosphere Reserves jointly manage Biodiversity and economic activity.
Deforestation : The clearing of forests over a wide area is called deforestation.
Desertification : The process by which fertile land becomes desert is called desertification. Deforestation is the cause of desertification.
Ecosystem : An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment, interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows.
Endangered Species : The species which are facing the risk of extinction are called endangered species. the destruction of their natural habitats. Some examples of endangered animals are : Tiger, Snow leopard, Great Indian rhinoceros, Asiatic lion, Desert cat, Lion-tailed macaque, Namdapha flying squirrel, and Kashmir stag.
Endemic Species : Endemic species are those species which are found exclusively in a 'particular area'. Endemic species are restricted to a certain area. Endemic species are not found naturally anywhere . The plants such as sal and wild mango are found naturally only in the Pachmarhi Biosphere.
Extinct : Extinct or extinct species which no longer exist anywhere on the earth are called extinct species. Some of the examples of extinct species of animals are : Dinosaur, Dodo, Cave lion, Caspian tiger, and Irish deer.
Fauna : The animals of a particular area are called fauna of that area Thus, fauna means animals which are found naturally in that area. Cheetal, Wolf, Leopard, Chinkara, Blue bull, Barking and Wild dog are the examples of fauna of the Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve.
Flora : The plants of a particular area are called flora of that area Thus, flora means plants which are found naturally in that area. Teak, Jamun, Fern, San Mango and Arjan are the example flora of Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve
Migratory Birds : The birds which move from very cold regions to warmer regions in winter, and go back after the winter is over are called migratory birds. Migratory birds fly to far away places every year during a particular time because of climatic changes. The purpose of migration of birds is to survive.
National Park : A National Park is a relatively large area of scenic beauty protected and maintained by the Government to preserve flora and fauna (plants and animals), landscape, historic objects of the area and places of scientific interest. Another purpose of establishing National Parks is to provide human recreation and enjoyment.
Red Data Book : Red Data Book is the book which keeps a record of all the endangered animals, plants and other species. Actually, Red Data book contains a lot of species which are in danger of becoming extinct
Reforestation : The planting of trees in an area in which forests are destroyed, is called reforestation.
Sanctuary : A Wife Sanctuary is a protected area of land which is created for the protection of wild natural environment like forest tin which no bunting is permitted
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
Question 1:
Fill in the blanks:
(a) A place where animals are protected in their natural habitat is called ____________.
(b) Species found only in a particular area are known as ____________.
(c) Migratory birds fly to far away places because of ____________ changes.
Answer 1:
(a) A place where animals are protected in their natural habitat is called wildlife
sanctuary.
(b) Species found only in a particular area are known as Endemic species.
(c) Migratory birds fly to far away places because of climatic changes.
You May Also Like:
1. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar system
2. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
3. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
4. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
5. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell : Structure and Function
Question 2:
Differentiate between the following:
(a) Wildlife sanctuary and biosphere reserve
(b) Zoo and wildlife sanctuary
(c) Endangered and extinct species
(d) Flora and fauna
Answer 2:
(a) Wildlife sanctuary and biosphere reserve
(b) Zoo and wildlife sanctuary
(c) Endangered and extinct species
(d) Flora and fauna
Question 3:
Discuss the effects of deforestation on the following:
(a)Wild animals
(b)Environment
(c) Villages (Rural areas)
(d)Cities (Urban areas)
(e) Earth
(f) The next generation
Answer 3:
(a)Wild animals: Due to deforestation, the natural habitat of wild animals gets destroyed. The homeless wild animals fall prey to human beings and get killed. Moreover, due to deforestation, the wild animals and birds do not get enough food and starve to death. In this way, many wild animals become extinct (or vanish) from that area.
(b)Environment: Deforestation increases the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. This will lead to global warming. Global warming can melt polar ice caps rapidly, producing a tremendous amount of water Heading to a rise in the sea level. The raised sea-water level will flood the low-lying coastal areas causing loss of life and property.
(c) Villages (Rural areas) : The rural areas largely depend on forests for fuel, fruits, honey, gum, sealing wax, wood etc. Deforestation has reduced their resources and the uninhabited animals
are also a danger for the villagers.
(d)Cities (Urban areas) : Cities are not directly affected by deforestation. But the
changes in the climate results in calamities like flood and droughts which affect
the cities also. It also leads to global warming.
(e) Earth: Deforestation has converted the fertile lands into deserts. The natural
calamities like floods and droughts are also the result of deforestation. Deforestation leads to an increase in carbon dioxide (C02) concentration in the atmosphere and cause of climatic change.
(f) The next generation: Deforestation has affected our climate very much. Many
species are at the verge of extinction because of deforestation and some species are already extinct. Climatic conditions will be adversely affected. Environment will not be clean and healthy. It may have to suffer from the effects of global warming, no fuel and no paper etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
Question 4:
What will happen if:
(a)we go on cutting trees.
(b)the habitat of an animal is disturbed.
(c) the top layer of soil is exposed.
Answer 4:
(a)We go on cutting trees: If we go on cutting trees, it leads to,
(i) an increase in temperature of earth's atmosphere leading to global warming.
(ii) soil erosion making the soil infertile and lead to desertification.
(iii) frequent flooding of rivers leading to loss of life and property.
(iv) decrease in rainfall leading to droughts.
(b)The habitat of an animal is disturbed:
If the habitat of an animal is disturbed it becomes homeless. This homeless animal falls prey to human beings and gets killed. Moreover, due to disturbance of habitat, the wild animal does not get enough food and starve to death. In this way, the animal becomes extinct from that area.
(c) The top layer of soil is exposed: Top layer of the soil if fertile. If the top layer of soil is exposed, it will wash away by the falling rain water and erode rapidly. The removal of the top layer will gradually convert the fertile land into deserts. Moreover the eroded soil is carried by the flowing rainwater into rivers, resulting in decreasing the depth of rivers. As a result, the chances of floods will increase.
Question 5:
Answer in brief:
(a)Why should we conserve biodiversity?
(b)Protected forests are also not completely safe for wild animals. Why?
(c) Some tribals depend on the jungle. How?
(d)What are the causes and consequences of deforestation?
(e)What is Red Data Book?
(f) What do you understand by the term migration?
Answer 5:
(a) We should conserve biodiversity because each and every organism in nature plays an important role in balancing the natural system. If one of them vanishes then the ecosystem of that place will be destroyed.
(b) Protected forests are not completely safe for wildlife because some local people kill animals on a large scale for their valuable skin etc.
(c) Some tribals depend on the jungle because they get almost all of their resources to live from the jungle like shelter, wood, food, etc.
(d) The causes of deforestation are as follows:
(i) trees are cut down to obtain wood for using as fuel.
ii) trees are cut down to obtain wood (timber) for making doors, windows and furniture.
(iii) trees are cut down to obtain wood n for making paper.
(iv) trees are cut down to obtain more agricultural land for cultivation of crops for the ode increasing population.
(v) trees are cut down to get land for building houses, factories, roads and dams, etc.
(e)Red Data Book is the book which keeps a record of all the endangered animals, plants and other species. Actually, the Red Data Book contains a list of species (animals and plants) which are in danger of becoming extinct. There are different Red Data Books for plants, animals and other species. There is also a Red Data Book of India. Some of the endangered species of animals listed in the Red Data Book of India are : Flying squirrel, Indian giant squirrel, Blackbuck. Great Indian rhinoceros, Snow leopard, and Tiger. The advantage of maintaining Red Data Book is that we come to know which species of animals, plants, etc, are very small in number and facing the danger of extinction so that timely remedial steps can be taken by the Authorities concerned to prevent their extinction
(f) The process of a bird (or other animal) moving from one place to another according to the season is called migration. Alternatively, when a bird (or other animal) travels from one place to another in one season and returns in a different season, it is called migration. Migration of birds is an adaptation to escape the harsh and cold conditions of their normal habitat in winter so as to survive. Siberian crane is an example of a migratory bird.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
Question 6:
In order to meet the ever-increasing demand in factories and for shelter, trees are being continually cut. Is it justified to cut trees for such projects? Discuss and prepare a brief report.
Answer 6:
In order to meet the ever-increasing demand for wood in factories and for shelter (building houses,furniture, etc), forest trees are being cut continuously. It is quite justified to cut a limited number of trees for genuine developmental purposes. But at the same time, an equal number of new trees should be planted (in place of cut down trees) to maintain a balance in nature and avoid unpleasant consequences of deforestation.
So it is very important to plant more trees and to find out ways of recycling and restoring our natural wealth.
Question 7:
How can you contribute to the maintenance of green wealth of your locality? Make a list of actions to be taken by you.
Answer 7:
We can contribute to the maintenance of green wealth of our locality by taking these actions:
(i) Taking care of the plants and trees growing in our surroundings.
(ii) We have to encourage the people to plant more trees by informing them about the importance of growing trees.
(iii) Planting new trees is equally important as taking care of the existing trees.
iv) We should inform them about the consequences of deforestation and global warming.
(v) We should teach the small children and encourage the slogan one man one tree every year.
Question 8:
Explain how deforestation leads to reduced rainfall.
Answer 8:
The forest trees, absorbed ground water through their roots and then maximum of this absorbed water releases as water vapour into the atmosphere, by the process transpiration. This water vapour helps in bringing rain in that area. When the forest trees are cut down, then the lesser number of trees put less water vapour into the atmosphere through transpiration. Since less water vapour is put into the atmosphere, there is less rainfall in that area. When there is less rainfall in an area.
Question 9:
Find out the information about the national parks in your state. Identify and show their
location on the outline map of India.
Answer 9:
Do yourself.
Question 10:
Why should paper be saved? Prepare a list of ways by which you can save paper.
Answer 10:
Paper is made from wood pulp that is produced from the wood of forest trees. It has been estimated that 17 full grown trees are needed to make 1 tonne of paper. So, many trees have to be cut down from the forests to make paper. Paper making is another cause of deforestation. So, we should save paper to save the forest trees.
The ways by which we can save paper are:
(i) We should recycle the waste paper.
(ii) We should not litter paper here and there.
(iii) Paper should be sent through a proper channel for recycling.
(iv) We should not tear our old books and donate it to poor children so that they can
reuse those books.
(v) We should encourage buying recycled paper products.
(vi) We should avoid taking paper bags from the shops, instead we should carry jute bags.
Question 11:
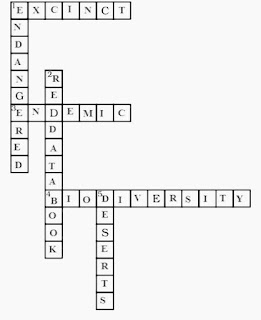
Complete the word puzzle:
Down
1. Species on the verge of extinction.
2. A book carrying information about endangered species.
5. Consequence of deforestation.
Across
1. Species which have vanished.
3. Species found only in a particular habitat.
4. Variety of plants, animals and microorganisms found in an area.
Answer 11.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals