NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
Features in Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light:
16 Light
16.1 What makes Things Visible
16.2 Laws of Reflection
16.3 Regular and Diffused Reflection
16.4 Reflected Light Can be Reflected Again
16.5 Multiple Images
16.6 Sunlight — White or Coloured
16.7 What is inside Our Eyes?
16.8 Care of the Eyes
16.9 Visually Impaired Persons Can Read and Write
16.10 What is the Braille System?
-------------------------------------------------------------
Board CBSE
-------------------------------------------------------------
TextBook NCERT
-------------------------------------------------------
CLASS Class 8
--------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Science
----------------------------------------------------------
CHAPTER Chapter 16
-------------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Light
--------------------------------------------------------------
Category NCERT Solutions
---------------------------------------------------------------
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
Keyword:
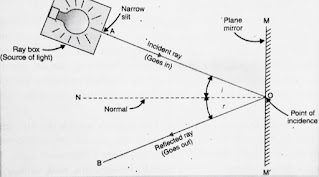
Angle of Incidence: The angle between incident ray and normal is called angle of incidence.
Angle of Reflection: The angle between reflected ray and normal is called angle of reflection.
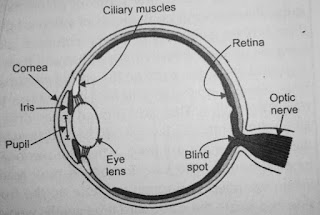
Blind Spot: It is the part of the eye where image does not form. Here rod cells and cone cells are absent.
Braille: Visually impaired persons can read and write
using the Braille system.
Cones: It is the light sensitive cell which helps to see in bright light.
Cornea: It is the part of the eye where image is formed.
Diffused or Irregular Reflection: When a parallel beam of rays falls on a rough surface, after reflection the rays are scattered in all directions. This type of reflection is called diffused or irregular reflection.
Incident Rays: In reflection, the rays which fall on a surface are called incident rays.
Iris: It is the part of the eye which gives colour to the eye.
KALEIDOSCOPE : Beautiful patterns are formed in a
kaleidoscope because of multiple reflections.
Lateral Inversion: The phenomenon of seeing right hand side as left hand side on mirror is called lateral inversion.
Laws of reflection: Two laws of reflection are
(i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
(ii) Incident ray, reflected ray and the normal drawn at the point of incidence to the reflecting surface, lying in the same plane.
Pupil: It is the part of the eye through which light can enter into the eye.
Reflected rays: In the reflection process, the rays which are reflected from the reflecting surface are called reflected rays.
Reflection: The process of returning back of the light to the same medium after striking the reflecting surface is called reflection.
Regular reflection: When the parallel beam of rays falls on a rough surface, after reflection they will scatter. This phenomenon is called regular reflection.
Rods: They are the light sensitive cells which helps us to see in dim light.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
Question 1:
Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see objects in the room? Can you see objects outside the room? Explain.
Answer 1:
When we are in the dark room, we do not see objects because there is no source of light. So no light is reflected from the objects and reaches to our eyes.
When we are outside the room, we can see the objects because there is a source of light. So light reflects from the objects and reaches to our eyes.
You May Also Like :
1. MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths
2. MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science
Question 2:
Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection. Does diffused reflection mean the
failure of the laws of reflection?
Answer 2:
Question 3:
Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take
place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
(a) Polished wooden table (b) Chalk powder
(c) Cardboard surface (d) Marble floor with water spread over it
(e) Mirror (f) Piece of paper.
Answer 3.
(a) The polished wooden table surface is an example of a smooth surface. We know that on a smooth surface, regular reflection occurs. So, on polished wooden surfaces, regular reflection occurs.
(b) Chalk powder is an example of rough surface and we know that on rough surface diffused reflection occurs. Hence on chalk powder diffused reflection occurs.
(c) The cardboard surface is an example of a rough surface and we know that on a rough surface, diffused reflection occurs. Hence, on cardboard surface diffused reflection occurs.
(d) The Marble floor with water spread over it acts as a smooth surface and on a smooth surface regular reflection occurs. Hence, regular reflection occurs on Marble floor with water spread over it.
(e) Mirror acts as a smooth surface and on a smooth surface regular reflection occurs. Hence, regular reflection occurs in a mirror.
(f) a piece of paper acts as a rough surface and on a rough surface diffused reflection occurs. Hence, diffused reflection occurs on a piece of paper.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
Question 4:
State the laws of reflection.
Answer 4:
Laws of reflection:
(i) The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
(ii) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the surface at the point of
incidence lies in the same plane.
Question 5:
Describe an activity to show that the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the points of incidence lie in the same plane.
Answer 5:
We take a plane mirror strip MM' and place it sideways on a white sheet of paper so that its reflecting surface is towards the left side. Now we mark the position of the mirror on the sheet of paper with a pencil.
Keep the ray box at position A, in front of the plane mirror. By opening the slit of ray box, shine a narrow beam of light AQ on the plane minor. We will see that the beam of light AO strikes the mirror surface at point O, it gets reflected and then goes in another direction OB. Now we mark the point on the sheet of paper and trace the paths of rays of light AO and OB on the sheet of paper by using a scale and pencil. At point O we draw a line ON perpendicular to the surface of the mirror MM’.
Let us measure the angles AON and NOB. We will find that the angle AON is equal to the angle NOB.
Now, the angle AON is the angle of incidence and the angle NOB is the angle of reflection, so this activity shows that the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. In this activity, the incident ray AO, the reflected ray OB and the normal ON, all lie in the plane of paper. They neither come up out of paper nor go down into paper. This shows that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal perpendicular at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
Question 6:
Fill in the blanks in the following:
(a) A person 1 m in front of a plane mirror seems to be _______________ m from his image.
(b) If you touch your ____________ ear with right hand in front of a plane mirror it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is touched with your ____________.
(c) The size of the pupil becomes ____________ when you see in dim light.
(d) Night birds have ____________ cones than rods in their eyes.
Answer 6:
(a) A person 1 m in front of a plane mirror seems to be 2 m from his image.
(b) If you touch your left ear with right hand in front of a plane mirror it will be seen in
the mirror that your right ear is touched with your left hand.
(c) The size of the pupil becomes large when you see in dim light.
(d) Night birds have less cones than rods in their eyes.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Light
Question 7:
Choose the correct option: Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
(a) Always
(b) Sometimes
(c) Under special conditions
(d) Never
Answer 7:
(a) Always
Question 8:
Choose the correct option: Image formed by a plane mirror is
(a) virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged
(b) virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object
(c) real at the surface of the mirror and enlarged
(d) real, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
Answer 8:
(b) virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object
Question 9:
Describe the construction of a kaleidoscope.
Answer 9:
The kaleidoscope is an instrument containing inclined plane mirrors which produce multiple reflections of coloured glass pieces (or coloured plastic places and create beautiful patterns). The kaleidoscope consists of three long and narrow strips of plane mirrors inclined at 60 to one another forming a hollow prism, and fitted into a cardboard tube. One end of the cardboard tube is closed by an opaque dise having a small hole at its centre. The other end of the cardboard tube is closed with two circular discs of glass, the inner disc being of transparent glass (clear glass) and the outer disc of ground glass. A number of small pieces of different glasses having different shapes are kept between the two glass discs.
Question 10:
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye.
Answer 10:
Question 11:
Gurmit wanted to perform Activity 16.8 using a laser torch. Her teacher advised her not to do so. Can you explain the basis of the teacher’s advice?
Answer 11:
Intensity of the laser beam is very high, as it carries a large amount of energy. It is harmful for eyes and can cause permanent damage. One should not look at laser beams directly or indirectly for a longer period.
Question 12:
Explain how you can take care of your eyes.
Answer 12:
(1) Wash our eyes at least twice a day with clean water.
(2) Too little light or too much light is bad for eyes. So, we should not read or right in dim light.
(3) We should not read a book too close of our eyes or too far from our eyes.
(4) We should raise our eyes from time to time while reading or writing or watching TV.
(5) We should protect our eyes from injuries and foreign bodies.
(6) We should regularly take a balanced diet which helps to protect our eyes by providing essential elements like vitamin A.
(7) We should check our eyes every 6 months.
Question 13:
What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected ray is at an angle of 90° to the incident ray?
Answer 13:
We know that angle of incident ray is equal to angle of reflected ray.
⇒ ∠𝑖 = ∠𝑟
But it is given that
∠𝑖 + ∠𝑟 = 90°
⇒ ∠𝑖 + ∠𝑖 = 90°
⇒ 2∠𝑖 = 90°
⇒ ∠𝑖 =(90°/2)
= 45°
Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
Question 14:
How many images of a candle will be formed if it is placed between two parallel plane mirrors separated by 40 cm?
Answer 14:
Infinite number of images.
Question 15:
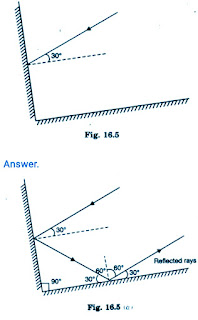
Two mirrors meet at right angles. A ray of light is incident on one at an angle of 30° as shown in Fig. 16.19. Draw the reflected ray from the second mirror.
Question 16:
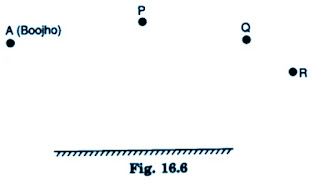
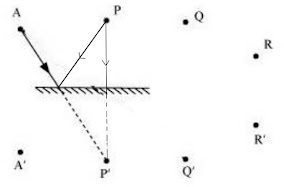
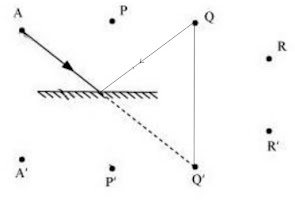
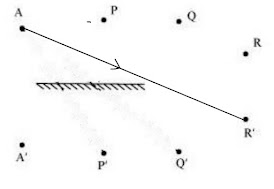
Boojho stands at A just on the side of a plane mirror as shown in Fig. 16.20. Can he see himself in the mirror? Also can he see the image of objects situated at P, Q and R?
Answer 16:
Boojho can't see his own image because he is not standing in front of the mirror.
He is able to see objects at P and Q because the rays coming from P and Q get reflected by the mirror and reach his eyes. The ray from object R does not reflect and reaches Boojho, so he cannot see object R.
(a)
(b)
Question 17.
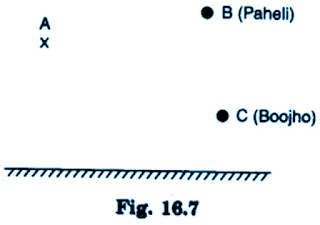
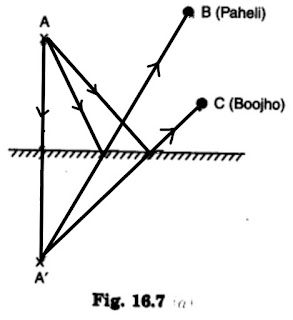
(a) Find out the position of the image of an object situated at A in the plane mirror (Fig. 16.7).
(b) Can Paheli at B see this image?
(c) Can Boojho at C see this image?
(d) When Paheli moves from B to C, where does the image of A move?
Answer 17:
(a) The image of the point A will be formed at A’ in such a way that the distance between mirror and A is equal to the distance between mirror and A’.
(b) Yes, Paheli can see the image of A.
(c) Yes, Boojho can see the image of A.
(d) When Paheli moves from B to C, the position of the image does not change.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light