NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions includes all NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science in form of pdf, worksheet free to download.
8. Cell — Structure Structure And And Functions
8.1 Discovery of the Cell
8.2 The Cell
8.3 Organisms show Variety
in Cell Number, Shape and
Size
8.4 Cell Structure and
Function
8.5 Parts of the Cell
8.6 Comparison of Plant and
Animal Cells
-------------------------------------------------------------
Board CBSE
-------------------------------------------------------------
TextBook NCERT
-------------------------------------------------------
CLASS Class 8
--------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Science
----------------------------------------------------------
CHAPTER Chapter 8
-------------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Cell Structure and Functions
--------------------------------------------------------------
Category NCERT Solutions
---------------------------------------------------------------
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions
Keywords Related with Cell Structure and Functions :
Cell : The cell (from Latin cella, meaning "small room") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known organisms. A cell is the smallest unit of life. Cells are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of cells is called cell biology, cellular biology, or cytology.
Cell Membrane : The cell membrane or the plasma membrane or the cytoplasmic membrane, and is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space) and protects the cell from outside.
Cell Wall : It is the outermost part of a plant cell. It is made up of cellulose. It is non-living. Cell wall present only in the plant cell.
Chloroplast : Chloroplasts are organelles that conduct photosynthesis, where the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight.
Chromosome : Chromosomes are thread-like structures located inside the nucleus of animal and plant cells. Each chromosome is made of protein and a single molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Passed from parents to offspring, DNA contains the specific instructions that make each type of living creature unique.
Cytoplasm : Cytoplasm is the gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of a cell. It is composed of water, salts, and various organic molecules. Some intracellular organelles, such the nucleus and mitochondria, are enclosed by membranes that separate them from the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotes : Eukaryotes are organisms whose bodies are made up of eukaryotic cells, such as protists, fungi, plants and animals. Eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a nucleus and organelles, and are enclosed by a plasma membrane.
Gene : A gene is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity. Genes are made up of DNA. Some genes act as instructions to make molecules called proteins. However, many genes do not code for proteins. In humans, genes vary in size from a few hundred DNA bases to more than 2 million bases.
Multicellular : An organism that is made up of many cells is said to be multicellular. Animals, plants, and fungi are multicellular organisms and often, there is specialization of different cells for various functions.
Nuclear Membrane : Nuclear membrane is a double-layered membrane that separates the contents of the nucleus from the rest of the cell.
Nucleolus : The nucleolus is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. The nucleolus is a region found within the cell nucleus that is concerned with producing and assembling the cell's ribosomes. Following assembly, ribosomes are transported to the cell cytoplasm where they serve as the sites for protein synthesis.
Nucleus : The nucleus is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Inside its fully enclosed nuclear membrane, it contains the majority of the cell's genetic material. This material is organized as DNA molecules, along with a variety of proteins, to form chromosomes.
Organ : An organ is a self-contained group of tissues that performs a specific function in the body. The heart, liver, and stomach are examples of organs in humans.
Organelles : An organelle is a subcellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell, much like an organ does in the body. Among the more important cell organelles are the nuclei, which store genetic information; mitochondria, which produce chemical energy; and ribosomes, which assemble proteins.
Plasma Membrane : The plasma membrane, or the cell membrane, provides protection for a cell. It also provides a fixed environment inside the cell. And that membrane has several different functions. One is to transport nutrients into the cell and also to transport toxic substances out of the cell.
Plastid : The plastid is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic Cyanobacteria. Examples include chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and leucoplasts.
Prokaryotes : A prokaryotic cell is a type of cell that does not have a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Organisms within the domains Bacteria and Archaea are based on the prokaryotic cell, while all other forms of life are eukaryotic. However, organisms with prokaryotic cells are very abundant and make up much of Earth’s biomass.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions
Pseudopodia : A pseudopodium or pseudopod (plural: pseudopodia or pseudopods) is a temporary cytoplasmic extension of an amoeboid cell, used for locomotion and ingestion of food. The name means literally ‘false foot’.
Tissue : Tissues are groups of cells that have a similar structure and act together to perform a specific function. The word tissue comes from a form of an old French verb meaning “to weave”. There are four different types of tissues in animals: connective, muscle, nervous, and epithelial.
Unicellular : A unicellular organism is an organism that consists of a single cell. This means all life processes, such as reproduction, feeding, digestion, and excretion, occur in one cell. Amoebas, bacteria, and plankton are just some types of unicellular organisms. They are typically microscopic and cannot be seen with the naked eye.
Vacuole : A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal and bacterial cells. The vacuole is an organelle in cells which functions to hold various solutions or materials. This includes solutions that have been created and are being stored or excreted, and those that have been phagocytized, or engulfed, by the cell. A vacuole is simply a chamber surrounded by a membrane, which keeps the cytosol from being exposed to the contents inside.
White Blood Cell(WBC) : White blood cells (WBCs), also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions
Exercises
Question 1:
Indicate whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F).
(a) Unicellular organisms have one-celled bodies. (T/F)
(b) Muscle cells are branched. (T/F)
(c) The basic living unit of an organism is an organ. (T/F)
(d) Amoeba has irregular shape. (T/F)
Answer 1:
(a) Unicellular organisms have one-celled bodies. (True)
Explanation: For example amoeba is an unicellular organism. All the metabolic activities are performed in that cell.
Hence a cell is called a structural and functional unit of life.
(b) Muscle cells are branched. (False)
Explanation: Muscle cells can contract and relax which helps us to move.
(c) The basic living unit of an organism is an organ. (False)
Correction: The basic living unit of an organism is a cell.
(d) Amoeba has irregular shape. (True)
Explanation: By changing the concentration of the cytoplasm amoeba can change their body shape and also can produce pseudopodia.
You May Also Like:
1. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
2. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
3. MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Stars and Solar System with Answers
4.NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar system
Question 2:
Make a sketch of the human nerve cell. What function do nerve cells perform?
Answer 2:
The nerve cell receives and transfers messages, thereby helping to control and coordinate the working of different parts of the body.
Question 3:
Write short notes on the following:
(a) Cytoplasm
(b) Nucleus of a cell
Answer 3:
(a) Cytoplasm
Definition: The transparent and jelly-like material which is present between the nucleus and the cell membrane is called cytoplasm.
Characteristics of cytoplasm:
(i) Cytoplasm is living.
(ii) It is transparent
(iii) Made up of elements like carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen.
(iv) Various cell organelles like ribosomes, mitochondria, golgi bodies, chloroplast etc. are suspended inside cytoplasm.
Function of cytoplasm:
(i) Most of the chemical reactions which take place in the cell mostly occur in the cytoplasm.
(ii) It helps exchange and storage of substances among cell organelles.
[cytoplasm and nucleus together is called protoplasm]
(b) Nucleus of a cell
Definition:
The central spherical dense round body in the centre of the cell suspended in the cytoplasm is called the nucleus.
Nucleus has four parts - nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, nucleolus, chromatin fibre.
Nuclear membrane: The membrane which separates the nucleus from cytoplasm is called nuclear membrane. It is the outermost part of the nucleus. This membrane is also porous and allows the movement of materials between the cytoplasm and the inside of the nucleus
Nucleoplasm: The jelly-like substance present inside the nuclear membrane is called nucleoplasm.
Nucleolus: The dense central part of nucleoplasm is called nucleolus.
Chromatin fibre Or Chromosome : The thread like structure present in nucleoplasm is called chromatin fibre Or chromosome. These carry genes which help in inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring.
Characteristics of nucleus:
(i) It is living.
(ii) It is generally spherical.
(iii) Located in the centre of the cell.
Function of the Nucleus:
(i) Control all the activities of the cell.
(ii) Help in inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions
Question 4.
Which part of the cell contains organelles?
Answer 4.
Cytoplasm.
Question 5.
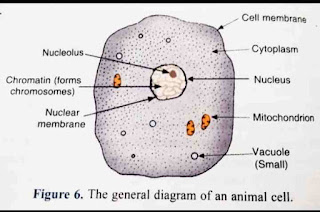
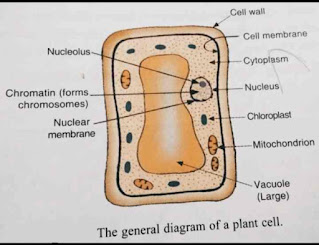
Make sketches of animal and plant cells. State three differences between them.
Answer 5.
Question 6.
State the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Answer 6.
Question 7.
Where are chromosomes found in a cell? State their functions.
Answer 7.
Chromosomes are found in the nucleus. The functions of chromosomes are to carry genes on them and to help to transfer the character from parents to the next generation.
Question 8.
‘Cells are the basic structural units of living organisms’. Explain.
Answer 8.
Since all the organisms that may be multicellular organisms or unicellular organisms, are made up of cells. So a cell is the structural unit of life.
Again all the cell activities or metabolic activities occurred in the cell. For unicellular organisms these activities occurred in one cell or for multicellular organisms these activities occurred in different sets of cells. Hence a cell is the functional unit of life.
Overall cell is the structural and functional unit of life.
Question 9.
Explain why chloroplasts are found only in plant cells?
Answer 9.
Chloroplast contains a green colour pigment called chlorophyll. This chlorophyll helps in photosynthesis. Since only plants can perform photosynthesis, chloroplasts are only found in plant cells.
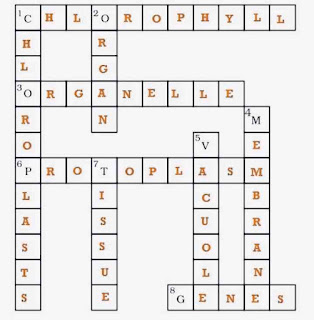
Question 10.
Complete the crossword with the help of clues given below:
Across
1. This is necessary for photosynthesis.
3. Term for component present in the cytoplasm.
6. The living substance in the cell.
8. Units of inheritance present on the chromosomes.
Down
1. Green plastids.
2. Formed by collection of tissues.
4. It separates the contents of the cell from the surrounding medium.
5. Empty structure in the cytoplasm.
7. A group of cells.
Answer 10.
Across
1. Chlorophyll
3. Organelle
6. Protoplasm
8. Genes
Down
1. Chloroplasts
2. Organ
4. Membrane
5. Vacuole
7. Tissue
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions