NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame include all NCERT Solutions for Class 8 in form of pdf, worksheet free to download.
Topics to Read in this Class 8 Science Lesson:
6. Combustion And Flame
6.1 What is Combustion?
6.2 How Do We Control Fire?
6.3 Types of Combustion
6.4 Flame
6.5 Structure of a Flame
6.6 What is a Fuel?
6.7 Fuel Efficiency
-------------------------------------------------------------
Board CBSE
-------------------------------------------------------------
TextBook NCERT
-------------------------------------------------------
CLASS Class 8
--------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Science
----------------------------------------------------------
CHAPTER Chapter 6
-------------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Combustion and Flame
--------------------------------------------------------------
Category NCERT Solutions
---------------------------------------------------------------
Keywords We Learn in NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame:
Acid Rain : Acid rain is a rain or any other form of precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). It can have harmful effects on plants, aquatic animals, and infrastructure. Acid rain is caused by emissions of sulphur dioxide dioxide and nitrogen oxide, which react with the water molecules in the atmosphere to produce acids.
Calorific Value : The amount of heat energy produced on complete combustion of 1 kg of a fuel is called its calorific value. The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in a unit called kilojoule per kg (kJ/kg).
Combustion : A chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen to give off heat is called combustion. The substance that undergoes combustion is said to be combustible. It is also called a fuel. Combustions are three types of: rapid combustion, spontaneous combustion and explosive combustion.
Deforestation : Cutting down of trees over a large area is called deforestation. Because of deforestation; soil-erosion, drought, and destruction of wildlife can cause.
Explosion : We generally have fireworks on festival days. When a cracker is ignited,
a sudden reaction takes place with the
evolution of heat, light and sound. A
large amount of gas formed in the
reaction is liberated. Such a reaction is
called explosion. Explosion can also take
place if pressure is applied on the
cracker.
Flame : A flame is the visible, gaseous part of a fire. It is caused by a highly exothermic reaction taking place in a thin zone. Very hot flames are hot enough to have ionized gaseous components of sufficient density to be considered plasma.
Fire Extinguisher : A fire extinguisher is an active fire protection device used to extinguish or control small fires, often in emergency situations.
Fuel : A substance that produces useful energy when it undergoes a chemical or nuclear reaction is called fuel. Fuel such as coal, wood, oil, or gas provides energy when burned.
Fuel Efficiency : Basically, fuel efficiency can be defined as the efficiency of the process in which thermal energy given to the fuel converts the chemical potential energy of the fuel to kinetic energy.
Global Warming : Global warming is the rise in temperature of the atmosphere of the earth. This results, among other things,
in the melting of polar glaciers, which leads to a rise in the sea level, causing floods in the coastal areas. Low lying coastal areas may even be permanently submerged under water.
Ideal Fuel : Ideal fuel is a fuel which on burning doesn't emit harmful gases it is easy to transport and store. It is also of very low cost and gives more heat per weight ,It also has a high calorific value. It should have low ignition temp. Ex. - Natural gas,LPG,CNG.
Ignition Temperature : The lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire is called its ignition temperature.
Inflammable Substances : The substances which have very low ignition temperature and can easily catch fire with a flame are called inflammable substances. Examples of inflammable substances are petrol, alcohol, Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG) etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
Exercises
Question 1:
List conditions under which combustion can take place.
Answer 1:
Conditions under which combustion can take place are as follows:
(i) Presence of fuel
(ii) Air (oxygen) is necessary.
(iii) temperature must be reached at its Ignition temperature.
You May Also Like:
1. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
2. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
3. MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Stars and Solar System with Answers
4. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter
5. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter
Question 2:
Fill in the blanks:
(a) Burning of wood and coal causes __________ of air.
(b) A liquid fuel, used in homes is __________.
(c) Fuel must be heated to its __________ __________ before it starts burning.
(d) Fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by __________.
Answer 2:
(a) Burning of wood and coal causes pollution of air.
(b) A liquid fuel, used in homes is Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG) .
(c) Fuel must be heated to its ignition temperature before it starts burning.
(d) Fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by water.
Question 3:
Explain how the use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities.
Answer 3:
CNG is a clean fuel which does not produce any harmful gases. Hence the use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities.
Question 4:
Compare LPG and wood as fuels.
Answer 4.
Question 5:
Give reasons:
(a) Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment.
(b) LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood.
(c) Paper by itself catches fire easily whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not.
Answer 5:
(a) Ordinary water conducts electricity to some extent. So, when water is thrown over the burning electrical appliance or burning electric wires, it can give electric shock to the persons involved in fire-fighting Thus, water cannot be used to extinguish fires caused by electricity,
(b) The calorific value of LPG is much higher than the calorific value of wood. This means that the burning of a given amount of LPG will produce much more heat than burning the same amount of wood. More than LPG is cheap and does not produce any ashes. So, LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood.
(c) Paper by itself catches fire easily whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not because the ignition temperature of paper is low as
compared to the paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe.
Question 6:
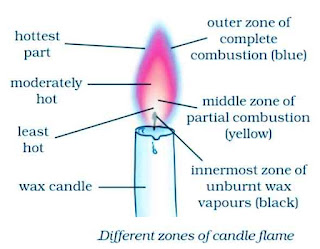
Make a labelled diagram of a candle flame.
Answer 6.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
Question 7:
Name the unit in which the calorific value of a fuel is expressed.
Answer 7:
The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in a unit called kilojoule per kg (kJ/kg).
Question 8:
Explain how CO2 is able to control fires.
Answer 8:
Carbon dioxide gas neither burns itself nor supports. Carbon dioxide gas is denser than air and forms a layer around the buming substances. Carbon dioxide layer covers the fire like a blanket due to which fresh air cannot reach the burning substances. The burning substance does not get oxygen of air and hence stops burning. In this way, the fire gets extinguished.
Question 9:
It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves but dry leaves catch fire easily. Explain.
Answer 9:
The ignition temperature of green leaves is higher than that of the dry leaves, so dry
leaves catch fire easily.
Question 10:
Which zone of a flame does a goldsmith use for melting gold and silver and why?
Answer 10:
In the outer zone of a flame, complete combustion of the fuel takes place because there is plenty of air around it. The outermost zone (or non-luminous zone) is the hottest part of the flame. Goldsmith uses the outermost zone of the flame for melting gold and silver.
Question 11:
In an experiment 4.5 kg of a fuel was completely burnt. The heat produced was measured to be 180,000 kJ. Calculate the calorific value of the fuel.
Answer 11:
Calorific value =
[ Heat produced (in kJ) / Mass of fuel (in kg) ]
= [180, 000 / 4.5]
= 40000 kJ/kg
Question 12:
Can the process of rusting be called combustion? Discuss.
Answer 12:
The process of rusting cannot be called combustion because neither release of energy nor heat and light are produced during it, while in combustion— release of energy takes place with heat and light.
Question 13:
Abida and Ramesh were doing an experiment in which water was to be heated in a beaker. Abida kept the beaker near the wick in the yellow part of the candle flame. Ramesh kept the beaker in the outermost part of the flame. Whose water will get heated in a shorter time?
Answer 13:
(ii) The fuel vapours burn partially in the middle zone because there is not enough air for burning in this zone. The partial (or incomplete) burning of fuel in the middle zone produces a moderate temperature.
In the outer zone of a flame, complete combustion of the fuel takes place because there is plenty of air around it. The outermost zone (or non-luminous zone) is the hottest part of the flame.
So Ramesh's water will get heated in a
shorter time.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame