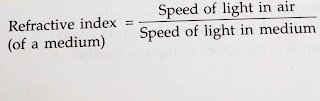Refraction of Light : Refraction, Laws of Refraction, Refractive Index
Refraction: The change in direction of the path of light, when it passes from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, is called refraction. Refraction of light is essentially a surface phenomenon.
You may Like
Why is refraction occurred?
Because when light travels from a optical optical medium to another optical medium its speed changes and due to changing in speed it is direction is also changes. Because of this refraction occurred.
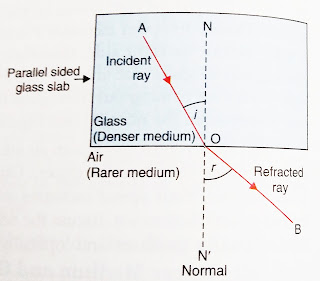
When a Ray of light travelling in one transparent medium strikes obliquely at the surface of another transparent medium, a part of light comes back to the same medium obeying the laws of reflection and is called the reflected light. The remaining part of the light passes Into the other medium and travels in a straight path different from its initial direction and is called reflected light.
Optical denser medium and optical rare medium :
When light travels from one medium to the another medium and its speed decreases then the first medium is called optically rarer medium and the second medium is called optically denser medium.
When light travels from one medium to another medium and its speed increases then the first medium is called optically denser medium and second medium is called optically rarer medium.
What happens when light travels from optically denser medium to optically rarer medium?
When light travels from optically denser medium to the optically rarer medium ( such as when light travels from water to air medium) then speed of light increases and the light move away from the normal.
What happens when light travels from optically rarer medium to optically denser medium?
When light travels from optically rarer medium to optically denser medium ( searchers when light travels from air to glass medium) speed of light decreases and it moves towards the normal.
What happens when a Ray of light incident normally on the surface separating the two media?
The Ray of light incident normally on the surface separating the two media, passes undeviated.
Laws of Refraction:
1. The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
2. The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence (i) to the Sine of angle of refraction (r) is constant for the pair of given medium.
That is, (sin i / sin r) = constant
This constant is known as refractive index.
Refractive Index :
The refractive index of second medium with respect to the first medium is defined as the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence in the first medium to the sine of the angle of refraction in the second medium.
Unit : the refractive index has no unit as it is the ratio of two similar quantities.
Relationship between refractive index and speed of light:
Refractive Index of a medium: the refractive index of a medium is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in vacuum or air to the speed of light in that medium
Absolute refractive index: the refractive index of a medium is generally defined with respect to vacuum then it is termed as absolute refractive index.
The refractive index of a transparent medium is always greater than 1 because speed of light in any medium is always less than in vacuum.
Write the conditions for a light ray to pass undeviated on refraction.
1) when the angle of incidence at the boundary of two media is zero.
2) when the refractive index of medium 2 is same as that of medium 1.
When a ray of light passes from one medium to the another medium then its speed , wevelength are changes but frequency remain same
Factors on which Refractive Index of a medium depend:
1) nature of the medium : if the speed of light is comparatively lesser of a medium then refractive index of that medium is comparatively greater and vice versa.
2) physical condition such as temperature: when temperature increases than speed of light in that medium also increases, hence refractive index of that medium decreases
3) wevelength or the colour of light: speed of light in air or vacuum is same for define colour of light. But for a given medium, speed of different colour of light is different. Speed is maximum for red colour light and minimum for violet colour light. Show refractive index for a given medium is maximum for violet colour light and minimum for red colour light.
Refraction of light through a rectangular glass block:
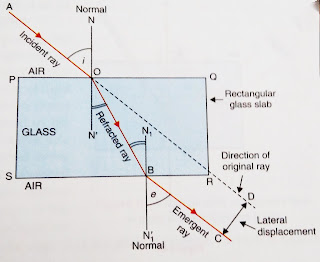
PQRS is a rectangular glass block. Incident ray AO falls on the surface PQ. NON' is a normal on the surface of PQ. Then refraction occurred at the surface of PQ and since light travels from air to glass that is optically rarer medium to optically denser medium, so AO bends towards the normal as OB and falls on the surface SR and again refraction occurred. Here light travels from optically denser medium to the optically rarer medium that is from glass medium to air medium. So, on refraction, light moves away from the normal and emerge as BC.Thus, the light emerges from a parallel sided glass slab in a direction parallel with that in which it enters the glass slab. Though the emergent ray BC is parallel to the incident ray AO, what the emergent ray has been sideways displaced or laterally displaced from the original path of the incident ray by a perpendicular distance CD. The perpendicular distance between the original path of incident ray and the emergent ray coming out of the glass slab is called lateral displacement of the emergent ray of light.
Lateral displacement depends on -
i) the thickness of the glass block : more the thickness of the medium, more is the lateral displacement.
ii) The angle of incidence: more the angle of incidence, more is the lateral displacement.
iii) The refractive Index of the glass : more the refractive index of the medium, more is the lateral displacement.