NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
Features in Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena:
15. Some Natural Phenomena
15.1 Lightning
15.2 Charging by Rubbing
15.3 Types of Charges and Their Interaction
15.4 Transfer of Charge
15.5 The Story of Lightning
15.6 Lightning Safety
15.7 Earthquakes
-------------------------------------------------------------
Board CBSE
-------------------------------------------------------------
TextBook NCERT
-------------------------------------------------------
CLASS Class 8
--------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Science
----------------------------------------------------------
CHAPTER Chapter 15
-------------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Some Natural Phenomena
--------------------------------------------------------------
Category NCERT Solutions
---------------------------------------------------------------
We Know the New KEYWORDS
CRUST: Outermost layer of the earth is called crust.
DISCHARGE: Discharge or electrical discharge is the release and transmission of electricity in an applied electric field through a medium such as a gas.
EARTH'S PLATES: The Earth is in a constant state of change. Earth's crust, called the lithosphere, consists of 15 to 20 moving tectonic plates. The plates can be thought of like pieces of a cracked shell that rest on the hot, molten rock of Earth's mantle and fit snugly against one another.
EARTHQUAKE: An earthquake is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere.
An earthquake is what happens when two blocks of the earth suddenly slip past one another. The surface where they slip is called the fault or fault plane. The location below the earth’s surface where the earthquake starts is called the hypocenter (focus), and the location directly above it on the surface of the earth is called the epicenter.
ELECTROSCOPE: The electroscope is an early scientific instrument used to detect the presence of electric charge on a body. It detects charge by the movement of a test object due to the Coulomb electrostatic force on it.
LIGHTNING: Lightning is an electrical discharge caused by imbalances between storm clouds and the ground, or within the clouds themselves.
LIGHTNING CONDUCTOR: A metal rod or wire fixed to an exposed part of a building or other tall structure to divert lightning harmlessly into the ground.
NEGATIVE CHARGE: Negative charge - having a surplus of electrons; having a lower electric potential. electric charge, charge - the quantity of unbalanced electricity in a body (either positive or negative) and construed as an excess or deficiency of electrons
POSITIVE CHARGE: Positive charge having a deficiency of electrons; having a higher electric potential. electric charge, charge - the quantity of unbalanced electricity in a body (either positive or negative) and construed as an excess or deficiency of electrons.
RICHTER SCALE: The Richter scale – also called the Richter magnitude scale or Richter's magnitude scale – is a measure of the strength of earthquakes.
SEISMOGRAPH: A seismograph, or seismometer, is an instrument used to detect and record earthquakes. Generally, it consists of a mass attached to a fixed base. During an earthquake, the base moves and the mass does not.
THUNDER: Thunder is the sound caused by lightning. Depending on the distance from and nature of the lightning, it can range from a sharp, loud crack.
THUNDERSTORM: Thunderstorm, a violent short-lived weather disturbance that is almost always associated with lightning, thunder, dense clouds, heavy rain or hail, and strong gusty winds. Thunderstorms arise when layers of warm, moist air rise in a large, swift updraft to cooler regions of the atmosphere.
TRANSFER OF CHARGE: Charge transfer which is basically transfer of electrons occurs when an electron relocates from an atom or molecule to another such entity. For this, one object should have free electrons or tendency to lose electrons and other should have affinity for the electron.
TSUNAMI: A tsunami is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake.
TREMOR: Shaking.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
Exercises
Question 1:
Which of the following cannot be charged easily by friction?
(a) A plastic scale
(b) A copper rod
(c) An inflated balloon
(d) A woollen cloth.
Answer 1:
(b) A copper rod
You May Also Like:
1. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
2. MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Stars and Solar System with Answers
3. MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Function with Answers
Question 2:
When a glass rod is rubbed with a piece of silk cloth the rod
(a) and the cloth both acquire positive charge.
(b) becomes positively charged while the cloth has a negative charge.
(c) and the cloth both acquire negative charge.
(d) becomes negatively charged while the cloth has a positive charge.
Answer 2:
(b) becomes positively charged while the cloth has a negative charge.
Question 3:
Write T against true and F against false in the following statements:
(a) Like charges attract each other (T/F)
(b) A charged glass rod attract a charged plastic straw (T/F)
(c) Lightning conductor cannot protect a building from lightning (T/F)
(d) Earthquakes can be predicted in advance (T/F)
Answer 3:
(a) Like charges attract each other (False)
Correction: Like charges repel each other
(b) A charged glass rod attract a charged plastic straw (True)
Explanation: Because a charged glass rod has some positive charges and a charged plastic straw has some negative charges. Positive and negative charges attract each other.
(c) Lightning conductor cannot protect a building from lightning (False)
Correction: Lightning conductors protect a building from lightning.
(d) Earthquakes can be predicted in advance (False)
Correction: Earthquakes can not be predicted in advance.
Question 4:
Sometimes, a crackling sound is heard while taking off sweaters during winters. Explain.
Answer 4:
It is an example of static electric discharge.
Generally, Sweater is made of wool and the other inner clothes like shirts are made up of cotton and synthetic fibres. When we try to take off the sweater, there is rubbing taking place between sweater and the inner clothes and they get charged. Due to accumulation of static charge on sweater, while taking off sweater, an electric discharge occurs between sweater
and the body which results in the formation of sparks and crackling sound.
Question 5:
Explain why a charged body loses its charge if we touch it with our hand.
Answer 5:
Our body is a good conductor of electricity and allows the passage of electric charge through our body to the earth. When we touch a charged body with our hands, the electric charge of that body is passed to the earth through our body. Hence a charged body loses its charge if we touch it with our hand.
Question 6:
Name the scale on which the destructive energy of an earthquake is measured. An
earthquake measures 3 on this scale. Would it be recorded by a seismograph? Is it likely to cause much damage?
Answer 6:
Richter Scale measures the destructive energy of an earthquake.
Yes, seismographs can measure an earthquake of magnitude 3 on the Richter Scale.
An earthquake measures 3 on the Richter scale is of low intensity and will not
cause any damage.
Question 7:
Suggest three measures to protect ourselves from lightning.
Answer 7:
Safety Measures during Lightning:
(i) No open space is safe during lightning. Take cover under a building.
(ii) When in open space, a person should never stand under a tree.
(iii) We should avoid raising an umbrella over our head during lightning.
(iv) We should switch off the TV sets during frequent lightning.
(v) During lightning, we should avoid touching the metal pipes fixed in a building or house.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
Question 8:
Explain why a charged balloon is repelled by another charged balloon whereas an uncharged balloon is attracted by another charged balloon?
Answer 8:
Two charged balloons have similar charges (negative charge) on the surfaces. Since like charges repel each other, that's why one charged balloon is repelled by another charged balloon.
When an uncharged balloon is brought near a charged one, because of electric induction, the uncharged balloon acquires some opposite charge. Since unlike charges attract each other, therefore a charged balloon attracts an uncharged one.
Question 9:
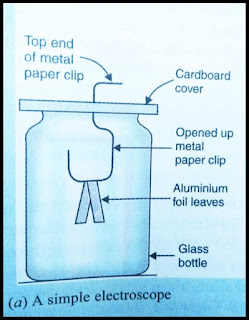
Describe with the help of a diagram an instrument which can be used to detect a charged body.
Answer 9:
We take an empty glass bottle. Then we take a piece of cardboard which is slightly bigger than the mouth of the glass bottle. Make a thin hole in the middle of the cardboard piece. Now we take a metal paper clip and open it up in such a way that it forms a shape of 5 (five) with a hook on the lower side. Now we insert this opened up metal clip in the hole made in cardboard pieces. Take a thin strip of aluminium foil about 5 centimetres long and 1 centimetre wide. Now we folded this aluminum foil in the middle and suspended it from the hook on the lower side of the opened up metal paper clip.
Now we have to place the cardboard piece carrying the metal clip and folded aluminium foil strip on the mouth of the glass bottle in such a way that the hook carrying the folded aluminium foil is inside the glass bottle. If we look at the folded aluminium foil strip kept on the metal hook it appears like two thin leaves of aluminium foil attached to the metal hook. In this situation, the two aluminium leaves are uncharged and lie close to each other.
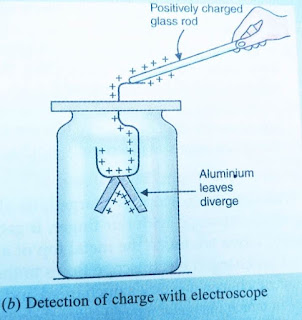
Now we charge a glass rod by rubbing its one end with a piece of silk cloth. Now we have to touch the charged glass rod with the top end of the metal clip. We will see that the two aluminium leaves move away from each other. We say that the aluminium leaves diverge or open up.
When we touch the top end of the metal clip with the positively charged glass rod then some of its positive charge is transferred to the top end of the metal clip. Now, since the metal clip is a good conductor of electricity, It conducts the positive electric charge to the two aluminium leaves held on its other end. In this way, the two aluminium leaves get charged with the same kind of electric charge-positive charge. We know that like charges repel each other. So, the two aluminium leaves having similar charges (positive charges) repel each other due to which they move apart or diverge.
From the above activity we conclude that when an object has some charge (positive charge or negative charge) , it will cause the aluminium leaves of the electroscope to diverge when touched with the metal top of the electroscope.
Question 10:
List three states in India where earthquakes are more likely to strike.
Answer 10:
Three states in India are Gujrat, Rajasthan and Himachal Pradesh.
In India, the areas most threatened are Kashmir, Western and Central Himalayas, the whole of North-East, Rann of Kutch, Rajasthan and the Indo – Gangetic Plain. Some areas of South India also fall in the danger zone.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
Question 11:
Suppose you are outside your home and an earthquake strikes. What precaution would you take to protect yourself?
Answer 11:
The precautions we should take when we outside the home during an earthquake are :
(i) we should stay at a clear spot away from buildings, trees and overhead power lines, etc. We should also sit on the ground.
(ii) If we are in a car (or bus), we should not come out of it. The car (or bus) should be driven slowly to a clear spot away from buildings, trees and overhead electric wires, etc. We should not come out of the
vehicle till the tremors stop,
Question 12:
The weather department has predicted that a thunderstorm is likely to occur on a certain day. Suppose you have to go out on that day. Would you carry an umbrella? Explain.
Answer 12:
Carrying an umbrella is not a good idea at all during thunderstorms. Because when we raise the umbrella over our head, lightning may strike the top end of the metal rod of the umbrella and harm us.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena