NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management includes all the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science in pdf, worksheet which is free to download.
Topics to Learn Here:
1. Crop Production and Management
1.1 Agricultural Practices
1.2 Basic Practices of Crop Production
1.3 Preparation of Soil
1.4 Sowing
1.5 Adding Manure and Fertilisers
1.6 Irrigation
1.7 Protection from Weeds
1.8 Harvesting
1.9 Storage
1.10 Food from Animals
-------------------------------------------------------------
Board CBSE
-------------------------------------------------------------
TextBook NCERT
-------------------------------------------------------
CLASS Class 8
--------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Science
----------------------------------------------------------
CHAPTER Chapter 1
-------------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Crop Production and Management
--------------------------------------------------------------
Category NCERT Solutions
---------------------------------------------------------------
Keywords Learn in NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management :
Agricultural : Agriculture is the art and science of cultivating the soil, growing crops and raising livestock. It includes the preparation of plant and animal products for people to use and their distribution to markets. Agriculture provides most of the world's food and fabrics.
Agricultural Practices : Cultivation of crops involves several activities undertaken by farmers over a period of time. These activities or tasks are referred to as agricultural practices
The various agricultural practices of crop production involves :
• Preparation of soil
• Protection from weeds
• Sowing
• Harvesting
• Adding manure and fertilizer
• Storage
• Irrigation
Animal Husbandry : Food is also obtained from animals for which
animals are reared. This is called animal
husbandry.
Crop : Same kind of plants cultivated at a place constitute a crop.
Fertiliser : Fertilicer is an inorganic salt which contains necessary plant nutrients. Fertiliser contains a rich amount of nutrients like nitrogen. phosphorus and potassium in concentrated form. Fertilisers are prepared in the factories.Fertiliser does not provide humus to the soil. Fertilisers are highly soluble in water and readily absorbed by the plants,
Granaries : A building or storeroom for storing threshed grain , farm feed , etc.
Harvesting : Harvesting is the cutting of the mature crop manually or by machines.
Irrigation : Supply of water to crops at appropriate intervals is called irrigation.
Kharif : The crops which are
sown in the rainy season are called
kharif crops. The rainy season in India
is generally from June to September.
Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut and
cotton are kharif crops.
Manure : Manure is a natural substance obtained by the decomposition of animal wastes like cow dung, human waste and plant residues.
Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients.Manures are prepared in the field by decomposing wastes. Manure provides humus to the soil in large amounts.Manures are not soluble in soil, therefore absorbed by plants at a very slow rate.
Plough : A large farming implement with one or more blades fixed in a frame, drawn over soil to turn it over and cut furrows in preparation for the planting of seeds.
Rabi : The crops grown in the
winter season (October to March) are
called rabi crops. Examples of rabi
crops are wheat, gram, pea, mustard
and linseed.
Seeds : A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering. The formation of the seed is part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosperm plants.
Silo : A silo is a structure for storing bulk materials. Silos are used in agriculture to store grain or fermented feed known as silage. Silos are commonly used for bulk storage of grain, coal, cement, carbon black, woodchips, food products and sawdust.
Sowing : The process of scattering seeds for putting seeds) in the ground soil for growing the crop plants is called sowing.
Seeds are sown in the soil either by hand or by seed drill. Thus, there are two methods of sowing the seeds in the soil. These are (1) Sowing by hand, and (2) Sowing with a seed drill.
Storage : The action or method of storing crops for future use.
Threshing : Separation of the grains from the chaff is called threshing.
Weeds : The undesirable plants or wild plants which grow along with a cultivated crop are called weeds.
Weedicide : The poisonous chemicals which are used to kill weeds (unwanted plants) in the fields are called weedicides. Some of the common weedicides are : 2,4-D, MCPA and Butachlor.
Winnowing : The process of separating grain from chaff and hay with the help of wind is called winnowing.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
Exercises
Question 1:
Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____________.
(b) The first step before growing crops is _____________ of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would _____________ on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and _____________ and _____________ from the soil are essential.
Answer 1:
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called crop.
(b) The first step before growing crops is preparation of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would float on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and water and nutrients from the soil are
essential.
You May Also Like:
1. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Function
2. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar system
3. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
4.NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
5. NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Motion and Time
Question 2:
Match items in column A with those in column B.
Answer 2:
Question 3:
Give two examples of each.
(a) Kharif crop
(b) Rabi crop
Answer 3:
(a) The example of kharif crops are paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut, cotton, etc.
(b) athe examples of rabi crops are wheat, gram, pea, mustard, etc.
Question 4:
Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil (b) Sowing
(c) Weeding (d) Threshing
Answer 4:
(a) Preparation of soil : Preparation of soil It is the first step before sowing the crop. In this step, first the soil is ploughed to loosen it and make it aerated which allows the roots to breathe easily. This also helps earthworms and microbes in the soil that bring the nutrient rich soil to the top. The process of loosening and turning of soil is called tilling or ploughing, which is followed by levelling and manuring.
(b) Sowing: The process of scattering seeds or putting seeds in the ground soil for growing the crop plants is called sowing. Traditionally, funnel-like tools are used for sowing. But now-a-days, seeds are sown by a seed drill implement. It scatters the seeds at regular intervals in the soil.
Precautions for sowing seeds:
(i) The seeds should be sown at the right depth in the soil suitable for germination.
(ii) The seeds should be sown at right intervals or spacings.
(iii) The seeds should not be sown in a dry soil.
(iv) The seeds should not be sown in a highly wet soil.
(c) Weeding: The process of removing weeds (unwanted plants) from a crop field is called weeding. Weeding is necessary because weeds compete with crop plants for water, nutrients, light and space, and hence affect the growth of the crops.
The various methods of weeding are
(i) Removal of weeds by pulling them out with hand.
(ii) Removal of weeds by using a trowel (khurpa).
(iii) Destroying the weeds by spraying special chemicals called weedicides
(d) Threshing: The process of beating out the grains from the harvested crop plants is called threshing. Threshing is done to take out the grain from its outer covering called chaff. This is carried out with the help of a machine called combine that is a combination of a harvester and thresher.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
Question 5:
Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Answer 5:
Question 6:
What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Answer 6:
The process of supplying water to crops at different intervals is called irrigation.
The two methods of irrigation which conserve water are as follows:
(i) Sprinkler system : In this system, there is a main pipeline laid in the field and attached with revolving nozzles at regular intervals. Water from the resources like tubewell escapes from rotating nozzles and is sprinkled like rain on the crops. This system of irrigation is useful on uneven land where sufficient water is not available and in sandy soil.
(ii) Drip system : In this system, a network of narrow pipes or tubes is laid down in the field with small holes. When water flows through the narrow pipes, it falls drop by drop just near the roots of plants.
In this method there is no wastage of water as water falls drop by drop, therefore this system of irrigation is very useful in regions where availability of water is poor. It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees.
Question 7:
If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Answer 7 :
Ans. Wheat is a rabi crop, so seeds need low temperature and less humidity to grow. If they are sown in kharif season, (ie, rainy season), the seeds would get destroyed due to excess water and would not grow.
Question 8:
Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Answer 8:
Soil supplies mineral nutrients to the crop. These nutrients are essential for the growth of plants. If crops are grown continuously in the same field, for a long period of time, the soil becomes poorer in nutrients. Thus, soil gets deficient in nutrients and the field becomes infertile.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
Question 9:
What are weeds? How can we control them?
Answer 9:
The unwanted plants or wild plants which grow naturally along with the cultivated crop are called weeds.
There are many ways to remove weeds and control their growth.
1. Removal of weeds by pulling them out with hand : Weeds can be removed from the crop fields just by pulling them up with hands. When we pull the weeds, they get uprooted from the field. These uprooted weeds can then be thrown away,
2. Removal of weeds by using a trowel (khurpi) : Weeds can be removed by digging or cutting them close to the ground frequently with the help of an implement called trowel or khurpi.
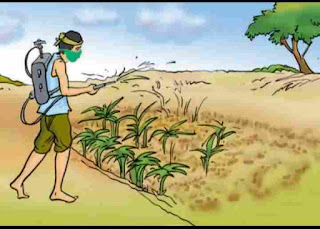
3. Destroying the Weeds by Spraying Special Chemicals Called Weedicides : Some of the common weedicides are : 2,4-D, MCPA and Butachlor. A solution of the weedicide in water is sprayed on the standing crops in the fields with a sprayer . The weedicides kill and destroy the weeds but do not damage the main crop.
Question 10:
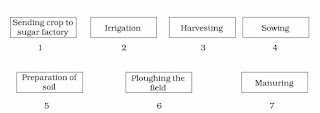
Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
Answer 10:
Preparation of Soil → Ploughing the Field → Sowing → Manuring → Irrigation → Harvesting → Sending crop to a Sugar Factory.
Question 11 :
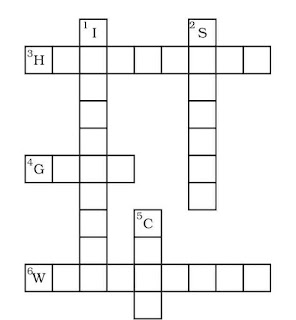
Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.
Down
1. Providing water to the crops.
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5. Certain plants of the same kind are grown on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from chaff.
Answer 11:
Down
1. Irrigation
2. Storage
5. Crop
Across
3. Harvester
4. Gram
6. Winnowing
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management