NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum includes all the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science in pdf, worksheet form which is free to download.
Topics Learn Here About NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum:
5 Coal and Petroleum
5.1 Coal
5.2 Petroleum
5.3 Natural Gas
5.4 Some Natural Resources are Limited
-------------------------------------------------------------
Board CBSE
-------------------------------------------------------------
TextBook NCERT
-------------------------------------------------------
CLASS Class 8
--------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Science
----------------------------------------------------------
CHAPTER Chapter 5
-------------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Coal and Petroleum
--------------------------------------------------------------
Category NCERT Solutions
---------------------------------------------------------------
Keywords we know now :
Coal : Coal is a fossil fuel, formed from vegetation, which has been consolidated between other rock strata and altered by the combined effects of pressure and heat over millions of years to form coal seams. The energy we get from coal today comes from the energy that plants absorbed from the sun millions of years ago.
Coal Gas : Coal gas, gaseous mixture—mainly hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide—formed by the destructive distillation (i.e., heating in the absence of air) of bituminous coal and used as a fuel.
Coal Tar : Coal tar is a thick dark liquid which is a by-product of the production of coke and coal gas from coal. It has both medical and industrial uses.
Coke : Coke is a grey, hard, and porous fuel with a high carbon content and few impurities, made by heating coal or oil in the absence of air—a destructive distillation process.
Fossil Fuel : A fossil fuel is a fuel formed by natural processes, such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms, containing organic molecules originating in ancient photosynthesis that release energy in combustion. Example : coal, petroleum.
Natural Gas : Natural gas, colourless highly flammable gaseous hydrocarbon consisting primarily of methane and ethane. It is a type of petroleum that commonly occurs in association with crude oil.
Petroleum : Petroleum is a naturally occurring material in the earth composed predominantly of chemical compounds of carbon and hydrogen with and without other nonmetallic elements such as sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen.
Petroleum Refinery : An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is transformed and refined into useful products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene, liquefied petroleum gas.
ncert solutions for class 8 science chapter 5 coal and petroleum
Exercises
Question 1:
What are the advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels?
Answer 1:
The advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels are:
(i) CNG and LPG burns easily.
(ii) CNG and LPG have a high calorific value.
(iii) CNG and LPG burns with a smokeless flame, so it does not cause air pollution
(iv) CNG and LPG do not produce any harmful gases.
(v) CNG and LPG does not leave behind any solid residue after burning
(vi) CNG and LPG are easy to handle and convenient to store.
You May Also Like:
1. ncert solutions for class 8 science chapter 8 cell structure and function
2.ncert solutions for class 8 science chapter 17 stars and the solar system
3. ncert solutions for class 8 science chapter 15 some natural phenomena
4. ncert solutions for class 8 science chapter 16 light
5. ncert solutions for class 8 science chapter 6 combustion and flame
Question 2:
Name the petroleum product used for surfacing of roads.
Answer 2:
Bitumen is the petroleum product used for surfacing of roads.
Question 3:
Describe how coal is formed from dead vegetation. What is this process called?
Answer 3:
Coal was formed by the decomposition of large land plants and trees buried under the earth about 300 million years ago. About 300 million years ago, the earth had dense forests in low lying wetland areas. Due to natural processes like earthquakes, volcanoes these forests were buried under the surface of earth. As more soil deposited over them, they were compressed. The temperature also rose as they sank deeper and deeper. Because of high pressure and high temperature deep inside the earth, and in the absence of air, the wood of buried forest plants and trees was slowly converted into coal.
The coal is formed from dead vegetation by the process called carbonisation.
Question 4:
Fill in the blanks:
(a) Fossil fuels are ___________, __________ and ___________.
(b) Process of separation of different constituents from petroleum is called __________.
(c) Least polluting fuel for vehicles is ___________.
Answer 4:
(a) Fossil fuels are Natural Gas, Coal and Petroleum.
(b) Process of separation of different constituents from petroleum is called refining.
(c) Least polluting fuel for vehicles is CNG.
Question 5:
Tick True/False against the following statements:
(a) Fossil fuels can be made in the laboratory. (T/F)
(b) CNG is more polluting fuel than petrol. (T/F)
(c) Coke is almost a pure form of carbon. (T/F)
(d) Coal tar is a mixture of various substances. (T/F)
(e) Kerosene is not a fossil fuel. (T/F)
Answer 5:
(a) Fossil fuels can be made in the laboratory. (False)
Explanation: As Fossil fuels can be made by natural process.
(b) CNG is more polluting fuel than petrol. (False)
Explanation: As CNG is a clean fuel. It is less polluting fuel than petrol.
(c) Coke is almost a pure form of carbon. (True)
Explanation: As coke is formed by heating coal in the absence of air.
(d) Coal tar is a mixture of various substances. (True)
Explanation: As coal tar is a mixture of 200 substances.
(e) Kerosene is not a fossil fuel. (False)
Explanation: Kerosene is a fossil fuel as it is obtained from petroleum.
Question 6:
Explain why fossil fuels are exhaustible natural resources.
Answer 6:
Ans. Fossil fuels are formed over a period of millions of years, by the action of high
temperature and high pressure on the remains of dead plants and animals. These are present in limited quantity beneath the earth. Thus, it will come to an end by human activities, and cannot be recreated in a short period of time. Thus fossil fuels are exhaustible natural resources.
Question 7:
Describe characteristics and uses of coke.
Answer 7:
Characteristics of coke are
(i) it is a tough porous and black substance.
(ii) It is produced by destructive distillation of coal.
(iii) It is an almost pure form of carbon.
The uses of coke are,
(i) It is used as domestic as well as an industrial fuel in stoves and furnaces.
(ii) It is used in the manufacture of steel.
(iii) It burns without producing smoke.
(iv) It is used as a reducing agent in the extraction of metals.
(v) It can be used to make fuel gases.
Question 8:
Explain the process of formation of petroleum.
Answer 8:
Petroleum was formed from the remains of plants and animals buried under the sea by the decomposition, millions of years ago
As millions of years ago, the plants and animals which lived in the sea, died and their bodies settled at the bottom of the sea and got covered with mud, sand and clay. Because of high temperature, high pressure and absence of air, these were slowly converted into petroleum and natural gas.
In the given figure, we see the deposits of petroleum and natural gas. The layer containing petroleum oil and gas is above that of water. It is because oil and gas are lighter than water and do not mix with it.
Petroleum is extracted by drilling holes (oil wells) in the earth's crust.
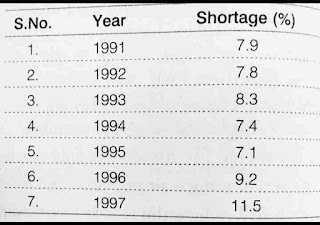
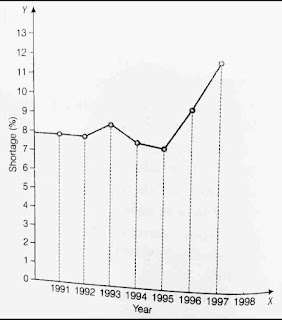
Question 9:
The following Table shows the total power shortage in India from 1991– 1997. Show the data in the form of a graph. Plot shortage percentage for the years on the Y-axis and the year on the X-axis.
Answer 9.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum