NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System is a part of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science. In this blog you get NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chap 17 Stars and the Solar System
17. Stars And The Solar System
17.1 The Moon
17.2 The Stars
17.3 Constellations
17.4 The Solar System
17.5 Some Other Members of the Solar System
-------------------------------------------------------------
Board CBSE
-------------------------------------------------------------
TextBook NCERT
-------------------------------------------------------
CLASS Class 8
--------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Science
----------------------------------------------------------
CHAPTER Chapter 17
-------------------------------------------------------------
SUBJECT Stars and the Solar System
--------------------------------------------------------------
Category NCERT Solutions
---------------------------------------------------------------
Keywords related to the lesson Stars And The Solar System
Artificial Satellites: An artificial satellite is an object that people have made and launched into orbit using rockets. There are currently over a thousand active satellites orbiting the Earth. The size, altitude and design of a satellite depend on its purpose.
Asteroids: Asteroids are minor planets, especially of the inner Solar System. Larger asteroids have also been called planetoids.
Cassiopeia: Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivaled beauty.
Celestial Objects: In astronomy, an astronomical object or celestial object is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe.
Comets: A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail.
Constellations: A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived outline or pattern, typically representing an animal, mythological person or creature, or an inanimate object.
Light Year: A unit of astronomical distance equivalent to the distance that light travels in one year, which is 9.4607 × 1012 km
Meteors: A meteoroid is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.
Meteoroids are significantly smaller than asteroids, and range in size from small grains to one-meter-wide objects.
Natural Satellites : A natural satellite, or moon, is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet or minor planet.
In the Solar System, there are six planetary satellite systems containing 205 known natural satellites.
Orbit : The fixed path along which the planets are moved around the sun.
Orion : Orion is a prominent constellation located on the celestial equator and visible throughout the world. It is one of the most conspicuous and recognizable constellations in the night sky. It is named after Orion, a hunter in Greek mythology.
Phases Of Moon : Different shapes of the moon is called phases of moon.
Planets : The heavenly bodies which moved around the sun are called planets.
Pole Star : A pole star or polar star is a star, preferably bright, nearly aligned with the axis of a rotating astronomical body. Currently, Earth's pole stars are Polaris.
Remote Sensing : Remote sensing is the science of obtaining information about objects or areas from a distance, typically from aircraft or satellites.
Solar System : The Sun and the celestial bodies which
revolve around it form the solar system.
It consists of large number of bodies
such as planets, comets, asteroids and
meteors. The gravitational attraction
between the Sun and these objects
keeps them revolving around it.
Stars : Stars are celestial bodies that emit light of
their own. Our sun is also a star.
Ursa Major : Ursa Major is a constellation in the northern sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater she-bear," referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa Minor, the lesser bear.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chap 17 Stars and the Solar System
Exercises
Question 1:
Choose the correct answer in Question:
Which of the following is NOT a member of the solar system?
(a) An asteroid
(b) A satellite
(c) A constellation
(d) A comet
Answer 1:
(c) A constellation
You May Also Like:
1. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
2. MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and Solar System with Answers
3. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
Question 2:
Choose the correct answer in Question:
Which of the following is NOT a planet of the sun?
(a) Sirius
(b) Mercury
(c) Saturn
(d) Earth
Answer 2:
(a) Sirius
Question 3:
Choose the correct answer in Question:
Phases of the moon occur because
(a) we can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
(b) our distance from the moon keeps changing.
(c) the shadow of the Earth covers only a part of the moon's surface.
(d) the thickness of the moon’s atmosphere is not constant.
Answer 3:
(a) we can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
Question 4:
Fill in the blanks:
(a) The planet which is farthest from the Sun is ____________.
(b) The planet which appears reddish in colour is ____________.
(c) A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a ____________.
(d) A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as __________.
(e) Shooting stars are actually not ____________.
(f) Asteroids are found between the orbits of _________ and _________.
Answer 4:
(a) The planet which is farthest from the Sun is Neptune.
(b) The planet which appears reddish in colour is Mars.
(c) A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a Constellation.
(d) A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as Satellite.
(e) Shooting stars are actually not Stars.
(f) Asteroids are found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chap 17 Stars and the Solar System
Question 5:
Mark the following statements as true (T) or false (F):
(a) Pole Star is a member of the solar system. ( F/T)
(b) Mercury is the smallest planet of the solar system. ( F/T)
(c) Uranus is the farthest planet in the solar system. (F/T )
(d) INSAT is an artificial satellite. (F/T )
(e) There are nine planets in the solar system. ( F/T)
(f) Constellation Orion can be seen only with a telescope. ( F/T)
Answer 5:
(a) Pole Star is a member of the solar system. (F)
Correction: Pole Star is not a member of the solar system. Pole Star is a star and stars are not members of our solar system.
(b) Mercury is the smallest planet of the solar system. (T)
(c) Uranus is the farthest planet in the solar system. (F)
Correction: Neptune is the farthest planet in the solar system.
(d) INSAT is an artificial satellite. (T)
(e) There are nine planets in the solar system. (F)
Correction: There are eight planets in the solar system.
(f) Constellation Orion can be seen only with a telescope. (F)
Correction: Constellation Orion can be seen by naked eyes.
Question 6:
Match items in column A with one or more items in column B:
Answer 6:
Question 7:
In which part of the sky can you find Venus if it is visible as an evening star?
Answer 7:
Venus becomes visible after sunset that is why it is called the evening star. It appears in the western horizon.
Question 8:
Name the largest planet of the solar system.
Answer 8:
Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system.
[It is so large that about 1300 earths can be placed inside this giant planet. However, the mass of Jupiter is about 318 times that of our Earth.]
Question 9:
What is a constellation? Name any two constellations.
Answer 9:
Constellations are groups of stars that appear to form recognisable shapes.
Examples: Great Bear, Orion, Cassiopeia and Leo Major.
Question 10:
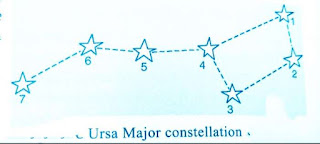
Draw sketches to show the relative positions of prominent stars in
(a) Ursa Major and (b) Orion
Answer 10:
Question 11:
Name two objects other than planets which are members of the solar system.
Answer 11:
Comets, Asteroids and Meteors.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chap 17 Stars and the Solar System
Question 12:
Explain how you can locate the Pole Star with the help of Ursa Major.
Answer 12:
We can locate the position of the Pole Star in the night sky with the help of the Ursa Major constellation. We have to look towards the northern part of the sky on a clear, moonless night during summer (at about 9 pm) and identify the Ursa Major constellation in the sky. Now we have to look at the two pointer stars at the end of the Ursa Major constellation. Imagine a straight line drawn through the two pointer stars of the Ursa Major constellation. Extend this imaginary line towards the north direction in the sky. This line will lead to a star which is not very bright. This star is the Pole Star.
Question 13:
Do all the stars in the sky move? Explain.
Answer 13:
the earth rotates on its axis from west to east. Therefore, all the stars in the sky (except the pole star) seem to move from east to west. With reference to Earth, pole star in the sky does not seem to move because it is located above the axis of rotation of the Earth in the north direction. It seems to remain stationary at a point in the sky.
Question 14:
Why is the distance between stars expressed in light years? What do you understand by the statement that a star is eight light years away from the Earth?
Answer 14:
The distances between the various stars are expressed in the unit of light year.
We normally express the large distances in the unit of kilometre. But the distances between the stars are so large that 'kilometre' becomes an extremely small and inconvenient unit to express such trge distances. For example, the various stars are millions of kilometres away, so kilometre unit is not suitable to express the distances between the stars. Thus, these large distances are expressed in light years.
One light year is the distance travelled by light in one year.
One light year = 9.46 × 1012 km.
If a star is eight light years away from the Earth. It means that the time taken by light to travel in eight years. So, the distance between the star and the Earth is given by
8 × (9.46 × 1012)km
= 7.6 × 1013 km.
Question 15:
The radius of Jupiter is 11 times the radius of the Earth. Calculate the ratio of the volumes of Jupiter and the Earth. How many Earths can Jupiter accommodate?
Answer 15:
Let the radius of the Earth be R.
So the radius of the Jupiter = 11R.
Volume of the earth = (4/3) πR³
Volume of the Jupiter
= (4/3) π(11R) ³
= 1331 × [ (4/3) πR³]
Therefore, Volume of the Jupiter : Volume of the Earth = 1331: 1
Since, the ratio of volumes is 1331:1, so Jupiter can accommodate 1331 Earths.
Question 16:
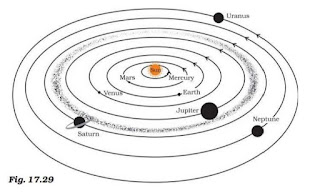
Boojho made the following sketch (Fig. 17.29) of the solar system. Is the sketch correct? If not, correct it.
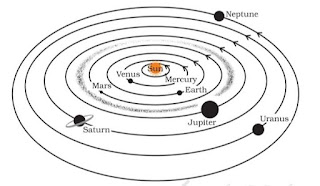
Answer 16:
Positions of Mars & Venus and Uranus & Neptune should be interchanged. The correct positions of the planets are as follows:
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chap 17 Stars and the Solar System