Sound class 8 Chapter 13 science CBSE NCERT
Sound class 8 Chapter 13 science CBSE NCERT with solution worksheet.
Sound is a form of energy which makes a perception of hearing.
Sound is produced by vibrating objects.
For example sound is produced by a vibrating bicycle Bell, sound is produced when a stretched rubber band vibrates, sound is produced when a cheater string vibrates, sound is produced when our vocal cords vibrate, sound is produced when the ear column enclosed in a a tube vibrates.
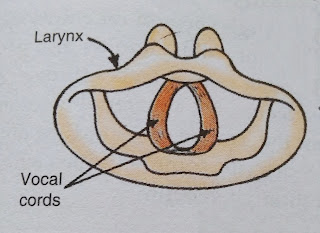
The human beings produce sound by using the voice box which is called larynx. The human voice box contains two ligaments known as vocal cords. Sound is produced by the vibrations of vocal cords. The lungs pass a current of air between the two vocal cords. This year makes the vocal cords vibrate. And the vibrating vocal cords produce sound.
Due to shorter vocal cords, the frequency of women's voice is higher than that of a man. For this reason the woman's voice is comparatively shriller than man.
Propagation of sound: the process by which sound travel from one place to another is called propagation of sound.
Sound needs a medium for its propagation. It can travel through solids liquids and gases. Sound cannot travel through vacuum. Since sound need material medium to propagate, show sound wave is an example of mechanical wave.
Sound travel fastest in solid medium and slowest in gaseous medium.
Speed of sound in air is 340 metres per second, in water is is 1500 metres per second, sound Travels at a speed of 5000 metres per second through iron.
If you want to hear a train approaching from for every, it is more convenient to put the ear to the railway track because the sound of train travels much more faster through solid railway track made of steel then through air.
Speed of light is much more faster than speed of sound. Because of this the flash of lightning is seen first and the sound of thunder is heard a little later.
Sound cannot be heard on the surface of moon because there is no air on the moon to carry the sound waves. Because of this, the astronauts who land on moon talk to each other through wireless sets using radio waves.
Amplitude, time period and frequency of a vibration:
Amplitude: the maximum displacement of A vibrating object from its Central position is called the amplitude of vibration. Unit of amplitude is metre.
Time period of vibration : the time taken by A vibrating object to complete one vibration is called its time period. Unit of time period is second.
Frequency of vibration: the number of vibrations made in one second is called the frequency of vibration. Unit of frequency is hertz.
Time period is equal to the reciprocal off frequency.
Time period = 1/ frequency
Characteristics of sound: loudness speech and quality
Two sounds can be distinguished from one another by three characteristics loudness, pitch and quality.
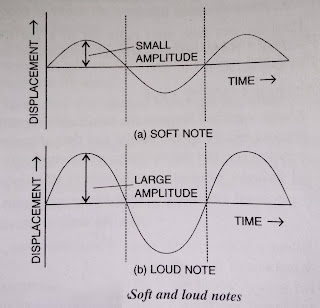
Loudness: loudness is the characteristic by virtue of which a loud sound can be distinguished from a faint one, both having the same pitch and quality.
Loudness of sound depends on the amplitude of the wave.
Factors affecting the loudness of sound
i) loudness is proportional to the square of the amplitude.
ii) loudness varies inversely as the square of distance from the source.
iii) loudness depends on the surface area of the vibrating body.
iv) loudness depends on the density of the medium.
v) loudness depends on the presence of resonant bodies.
Pitch:
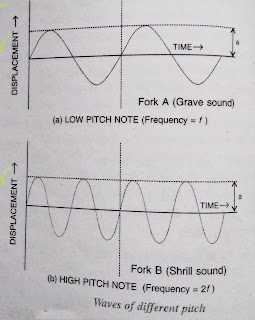
Peach is that characteristic of sound by which an acute or shrill note can be distinguished from a grave or flat note.
Speech of a note depends on its frequency. Two notes sounded on the same instrument with same amplitude, will differ in pitch when their vibrations are of different frequencies.
Quality:
Quality or timbre of a sound is that characteristic which distinguishes the two sound of the same loudness and same pitch, but emitted by two different instruments.
The quality of a musical sound depends on the web form.
Audible and Inaudible sound:
The sound which has frequency in between 20 hertz to 20000 hertz is called audible sound. This sound produce sensation of hearing.
The sound which has frequency below 20 hertz or or above 20000 hertz is called inaudible sound. This sound cannot produce sensation of hearing.
The sound which has frequency below 20 hertz is called infrasonic sound.
The sound which has frequency above 20000 hertz is called ultrasonic sound.
Uses of ultrasonic sound:
i) used as a diagnostic tool in medical science to investigate inside of the human body.
ii) used to study the growth of foetus.
iii) used in the treatment of muscular pain and a disease called arthritis.
iv) used to measure the depth of sea.
Music and Noise
Music: the present, continuous and uniform sound produced by the regular and periodic vibration is called music.
For example the sounds produced by a violin, piano, flute, tuning fork etc.
Noise: the sound produced by an irregular succession of disturbances and is usually a discontinuous sound is called noise.
For example the sound produced when a stone is thrown on a tin shade is a noise.
Difference between music and noise are:
1) music is regular, smooth and pleasant to the ears
Where does noise is harsh, discordant and unpleasant to the ears.
2) in music the web form is regular where does in noise the web form is irregular.
3) music ok is produced by the vibrations which are periodic where as noise is produced by an irregular succession of disturbances.
Musical instruments
Some musical instruments are,
i) stringed musical instruments such as Sitar Veena violin Tanpura.
ii) Wind musical instruments such as flute trumpet Shehnai
iii) membrane musical instruments such as tabla dholak drum.
iv) plate type musical instruments such as cymbals
Noise Pollution:
The presence of loud, unwanted and disturbing sounds in our environment is called noise pollution.
The cause of noise pollution are,
i) the motor vehicles running on the road to produce noise pollution by blowing horns and sounds of their engines.
ii) the brusting of crackers on various social and religious occasions produces noise pollution.
iii) the various machines in factories make loud sounds and cause noise pollution.
iv) the playing of loudspeakers and bands at marriages and other social functions cause noise pollution.
Harms of noise pollution:
i) Loud noise can cause great harm to our ears
ii) loud noise can cause a person to loss concentration in his work or studies.
iii) loud noise can cause irritation and headache.
iv) loud noise during night time disturbs our sleep.
Measures to control noise pollution:
i) we should not play radio, stereo systems and television too loudly.
ii) the horns of motor vehicles should not be blown unnecessarily
iii) the brusting of crackers should be avoided.
iv) loud speakers should be played at low volume during marriages and other social functions.