Class 8 Science : Light Solution (Part 1)
Class 8 Science : Light solution with question type answer for CBSE NCERT work sheet.
Light is a form of energy which helps us to see object around us.
We see an object when light falls on them and reflected back from it and reaches to our eye.
On basis of source of light, objects are two types of and they are are luminous object and non luminous object.
Luminous object are those objects which can emit light. For example Sun, star, candle ,tube light ,bulb.
Non luminous object are those objects which cannot emit light. For example book, pencil, chair, table.
Another name of non luminous object is illuminated object because they get illuminated or light up by the light of luminous objects falling on them.
When a non luminous object can be seen?
When light from luminous object falls on non luminous object and reflected back to our eyes then we see the non luminous object.
Reflection of light:
The process of sending back light rays which fall on the surface of an object, is called reflection of light
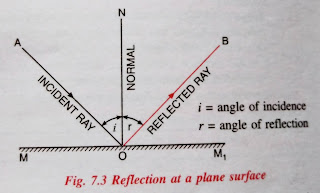
Incident ray : the ray of light which false on the reflector surface is called incident ray.
Reflected ray: the rray of light which is sent back by the reflector to the same medium is called the reflected Ray.
Point of incidence: the point at which the incident Ray strikes the reflector is called the point of incidence.
Normal: the perpendicular which is drawn at the point of incidence, on the reflector is called normal.
Incident angle or angle of incidence: the angle between incident Ray and normal is called angle of incidence.
Reflected angle or angle of reflection: the angle between the reflected Ray and normal is called angle of reflection.
Laws of Reflection of Light:
1) Incident Ray, reflected Ray and the normal are lie on the same plane.
2) incident angle is equal to the reflected angle.
<i = <r
Problem 1: if mother of incident angle is is 40 degree then what will be the measure of reflected angle?
Answer: measure of reflected angle is 40 degreedegree
Problem 2 : if some of measure of incident and reflected angle is 120 degree then what will be the measure of incident angle?
Answer: measure of incident angle= 120/2 = 60 degree.
Problem 3: A ray of light falls normally on the surface of a plane mirror. What will be the measure of incident angle and reflected angle and also write in which direction the reflected Ray will passes?
Answer: measure of incident angle is 0 degree because the incident Ray and normal lie on same straight line.
Since measure of incident angle is 0 degrees show according to law of reflection the reflected angle is also 0 degree.
The reflected ray travelled back along normal but in opposite direction.
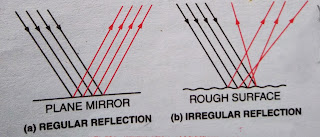
Regular Reflection: When parallel beam of rays fall on a smooth surface after reflection, they passes to the same medium in a particular direction as parallel beam of rays. This type of reflection is called regular reflection.
Because of Regular reflection image is formed.
Irregular Reflection or diffused reflection: When parallel beam of rays fall on a rough surface, after reflection the reflected rays will scattered in all direction. This type of reflection is called irregular reflection or or diffused reflection.
Because of irregular reflection object is seen.
Both the regular reflection and irregular reflection follow the laws of reflection.
Difference between regular reflection and irregular reflection
1) regular reflection occured on smooth surface and irregular reflection occured on rough surface.
2) after regular reflection parallel beam of rays still parallel to each other but in irregular reflection the parallel beam of rays are not parallel to each other after reflection.
3) because of Regular reflection image is formed whereas in irregular reflection object is seen.
Characteristics of image formed by a plane mirror:
1) image is virtual
2) the image is same size as the object.
3) the image is erect.
4) the image is laterally inverted.
5) the image formed in a plane mirror is the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
Multiple images
When two plane mirrors are kept inclined at an angle, they can form multiple images of an object , this is because the image of object formed in one plane mirror acts as an object for the other plane mirror.
If two planes are in client at an angle x, then number of images formed by the two Mirrors
=( 360°/ x) - 1
Example : i) if two Mirrors are inclined at 90 degree then number of images are
= (360 / 90) - 1
= 3
ii) if the two Mirrors are inclined at an angle of 60 degree then number of images =
(360/60) - 1 = 5
iii) if the Mirrors are in client at 120 degree, then number of images
(360/120) - 1 = 2
Hence, as the angle between two plane mirrors decreases, the number of images formed increases.
If an object is placed between two parallel plane mirrors facing each other, then theoretically an infinite number of images should be formed.
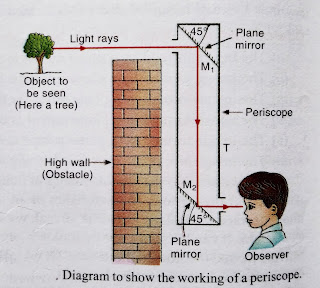
Kaleidoscope:
The scope is an instrument or toy containing inclined plane mirrors which are produce multiple reflections of coloured glass pieces and create beautiful patterns
Sunlight - white or coloured
Sun light is the source of light
The white light consists of seven colours and they are violet , Indigo , blue , green, yellow, orange and red.
What is Dispersion of light?
The splitting of white light into seven colours on passing through a transparent medium like a glass prism is called Dispersion of light.
Rainbow in the sky is a natural phenomenon showing the Dispersion of Sunlight