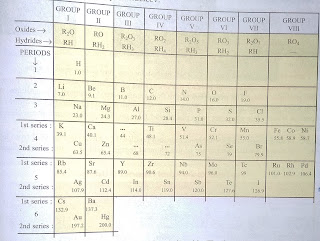
Periodic Table : Mendeleev's Law Definition Merits Demerits Short Notes PDF
Definition: the periodic table is a chart of elements prepared in such a way that the elements having similar properties of occur in the same vertical column or group.
The horizontal rows of periodic table called periods.
The vertical columns of the periodic table called groups.
Why is the predic table included the term periodic?
Answer: it is called priodic because the elements having similar properties are repeated after certain interval or periods.
Why is the periodic table has the term table?
Answer: it is called a table because the elements are arranged in the tabular form.
In Mendeleev's periodic table, the elements are arranged on the basis of their atomic masses and also on the similarity of chemical properties.
Whereas the Modern Periodic Table is based on the atomic numbers of elements.
State The Mendeleev's periodic table.
Or, write the Mendeleev's periodic law.
Answer: when elements are arranged in the order of increasing atomic masses, the elements with similar properties of air at regular intervals. The properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses.
In his periodic table, he arranged all the elements (63 elements found at that time) in the order of increasing atomic masses in horizontal rows but in such a way that elements having similar properties came directly under one another in the same vertical column or group. The similar properties used by Mendeleev to classify elements into groups are the similar formulae of their oxides and hydrides.
There were 7 periods ant 8 groups in the original periodic table of Mendeleev.
Out of 8 groups, First 7 groups are of normal elements and eighth group is of transition elements. Noble gases were not known at that time, hence there was no group of noble gases in Mendeleev's original periodic table.
We found two main features in his periodic classification: (1) gaps in the periodic table. (2) wrong order of atomic masses of some of the elements.
Mendeleef classify the 63 elements of that time on the basis of their (i) increasing atomic masses and (ii) grouping together the elements having similar properties.
(1) gaps in the periodic table: in order to make sure that the elements having similar properties sale in the same vertical column or group, Mendeleev left some gaps in his periodic table.
These gaps are left for the elements not known at that time. Mendeleev thought that this elements would be discovered letter on and even predicted the properties of these then unknown elements by studying the properties of the neighbouring elements. The missing elements of Mendeleev's periodic table where discovered letter on and their properties were found to be very close to those elements which were predicted by Mendeleev.
He called the undiscovered elements or unknown elements as Eka Boron, Eka aluminium, Eka silicon.
Letter when these elements were discovered then a eka-boron was named as scandium, Eka aluminium was named as gallium, Eka Silicon was named as Germanium.
(2) Wrong order of atomic masses of some of the elements: in order to make sure that the elements having similar properties fell in the same vertical column or group, mendeleef place a few elements in the wrong order of their atomic masses by keeping the element with higher atomic mass first and the element with lower atomic mass later.
As for example, he placed Cobalt before Nickel but Cobalt has atomic mass 58.9 ant Nikhil has atomic mass 58.7.
Merits of Mendeleev's periodic classification of elements:
(1) Mendeleev's periodic law predicted the existence of some elements that had not been discovered at that time.
(2) Mendeleev's periodic table could predict the properties of several elements on the basis of their positions in the periodic table.
(3) Mendeleev's periodic table could accommodate noble gases when they were discovered.
Limitation or demerits of Mendeleev's periodic classification of elements:
(1) the position of isotopes could not be explained.
(2) wrong order of atomic masses of some elements could not be explained.
(3) correct position could not be assigned to hydrogen in the periodic table.
The horizontal rows of periodic table called periods.
The vertical columns of the periodic table called groups.
Why is the predic table included the term periodic?
Answer: it is called priodic because the elements having similar properties are repeated after certain interval or periods.
Why is the periodic table has the term table?
Answer: it is called a table because the elements are arranged in the tabular form.
In Mendeleev's periodic table, the elements are arranged on the basis of their atomic masses and also on the similarity of chemical properties.
Whereas the Modern Periodic Table is based on the atomic numbers of elements.
State The Mendeleev's periodic table.
Or, write the Mendeleev's periodic law.
Answer: when elements are arranged in the order of increasing atomic masses, the elements with similar properties of air at regular intervals. The properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses.
In his periodic table, he arranged all the elements (63 elements found at that time) in the order of increasing atomic masses in horizontal rows but in such a way that elements having similar properties came directly under one another in the same vertical column or group. The similar properties used by Mendeleev to classify elements into groups are the similar formulae of their oxides and hydrides.
There were 7 periods ant 8 groups in the original periodic table of Mendeleev.
Out of 8 groups, First 7 groups are of normal elements and eighth group is of transition elements. Noble gases were not known at that time, hence there was no group of noble gases in Mendeleev's original periodic table.
We found two main features in his periodic classification: (1) gaps in the periodic table. (2) wrong order of atomic masses of some of the elements.
Mendeleef classify the 63 elements of that time on the basis of their (i) increasing atomic masses and (ii) grouping together the elements having similar properties.
(1) gaps in the periodic table: in order to make sure that the elements having similar properties sale in the same vertical column or group, Mendeleev left some gaps in his periodic table.
These gaps are left for the elements not known at that time. Mendeleev thought that this elements would be discovered letter on and even predicted the properties of these then unknown elements by studying the properties of the neighbouring elements. The missing elements of Mendeleev's periodic table where discovered letter on and their properties were found to be very close to those elements which were predicted by Mendeleev.
He called the undiscovered elements or unknown elements as Eka Boron, Eka aluminium, Eka silicon.
Letter when these elements were discovered then a eka-boron was named as scandium, Eka aluminium was named as gallium, Eka Silicon was named as Germanium.
(2) Wrong order of atomic masses of some of the elements: in order to make sure that the elements having similar properties fell in the same vertical column or group, mendeleef place a few elements in the wrong order of their atomic masses by keeping the element with higher atomic mass first and the element with lower atomic mass later.
As for example, he placed Cobalt before Nickel but Cobalt has atomic mass 58.9 ant Nikhil has atomic mass 58.7.
Merits of Mendeleev's periodic classification of elements:
(1) Mendeleev's periodic law predicted the existence of some elements that had not been discovered at that time.
(2) Mendeleev's periodic table could predict the properties of several elements on the basis of their positions in the periodic table.
(3) Mendeleev's periodic table could accommodate noble gases when they were discovered.
Limitation or demerits of Mendeleev's periodic classification of elements:
(1) the position of isotopes could not be explained.
(2) wrong order of atomic masses of some elements could not be explained.
(3) correct position could not be assigned to hydrogen in the periodic table.