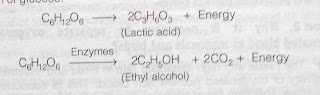Life Process Class 10 Ch 6 || NCERT Solution
Life Process class 10 chapter solution of NCERT book. Here get question answer in detail for Science .
NCERT page 95
Question 1. why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans?
Answer: multicellular organisms have to perform many activities for which large amount of energy required. show large amount of food needed to be breaks down which requires large amount of oxygen. But in diffusion process we get very small amount of oxygen which is insufficient for production of large amount of energy.
Question 2. What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive?
Answer: movement growth and respiration are necessary to identify whether something is alive.
Question 3. What are the outside raw materials used by an organism?
Answer. Nutrients water and oxygen are the raw materials obtained from outside.
Question 4. What processes would you consider essential for maintaining life?
Answer. The officers like nutrition respiration transportation excretion reproduction are essential for maintaining life.
NCERT text page 101
Question 1. What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition?
Answer
Question 2. where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
Answer. Water is absorbed by the roots from the soil.
Carbon dioxide is obtained from here through stomata.
Light is obtained from Sun.
Aadhar minerals like Iron Phosphorus magnesium Sulphur and nitrogen collected from the soil by the roots.
Question 3. What is the role of acid in our stomach?
Answer. The hydrochloric acid present in stomach creates an acidic medium which facilitates the action of enzyme pepsin. It kills the germs present in the food.
Question 4 what is the function of digestive enzymes?
Answer. digestive enzymes are the biological catalyst who's break down the complex food molecules into such small particles which can be absorbed from the alimentary canal into the blood stream..
Question 5. How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food?
Answer. The main reason for the absorption of digested food in digestive system is small intestine. The inner lining of small intestine is covered by Mini tiny finger like projections called villi. The presence of Villi gives the inner walls of the small intestine a very large surface area for absorption of digested food.
NCERT book solution page 115
Question 1 what advantages over an aquatic organism does a Terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Answer. The aquatic organisms use the oxygen dissolved in water for carrying out respiration
the amount of oxygen dissolved in water is limited. show the aquatic organisms have a much faster rate of breathing.
Terrestrial organisms take oxygen from atmosphere through respiratory organs. So, they have a much slower breathing rate than aquatic organism.
Question 2. what are the different ways in which glucose is oxidised to provide energy in various organisms?
Answer. Breaking down of glucose takes place in cytoplasm of the cell of all organisms. In this process three carbon molecule compound called pyruvate is produced.
Breaking down of glucose text place in various ways:
(I) anaerobic it is a process in which food is oxidized incompletely in absence of oxygen. For example, an aerobic respiration occur in skeletal muscles when we work hard for long time. During this process carbon dioxide, lactic acid ant energy is produced by the partial breakdown of glucose.
Aerobic respiration: it is the process in which food is completely oxidized in presence of oxygen and form large amount of energy along with carbon dioxide and water
Question 3. How is Oxygen and Carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
Answer : In human beings, oxygen is transported from lungs by the respiratory pigment called hemoglobin which is present in RBC that is red blood corpuscles. Haemoglobin has a very high affinity for oxygen. Carbon dioxide is more soluble in water than oxygen., most of carbon dioxide produced during respiration in the human body is transported in the dissolved form in our blood.
Question 4 how are the lungs designed in human beings to maximize the area for the exchange of gases?
Answer: in human lungs, there are millions of alveoli present. the president of millions of alveoli in lungs increases the surface area of absorption to greater extent. As a result exchange of gases takes place more.
NCERT chapter life process page 110
Question 1. What are the components of transport system in human beings? What are the functions of these components?
Answer. Human transport system consist of heart blood and blood vessels.
Function
(I) heart: it acts as a pumping organ to push and pull blood around the body. It receives the deoxygenated blood from various parts of the body and palms oxygenated blood throughout the body.
(ii) blood: it is a liquid connective tissue. It consists of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma.
Red blood cells: it helps in transportation of nutrients excretory materials hormones gases etc. oxygen is transported as oxyhaemoglobin and carbon dioxide as carbamino hemoglobin.
White blood cells: IIT fight against foreign bodies by producing antibodies and histamine.
Blood platelets: eat play an important role in coagulation of blood.
Blood vessel: blood vessels are a network of vessels. they help in the circulation of blood throughout the body.
Question 2: why it is necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds?
Answer. the mammals and birds are warm blooded animals which have high energy needs because they constantly require energy to maintain their body temperature. it is necessary to separate oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds because such a separation allows a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body cells which is required for producing a lot of energy needed by them.
Question 3. What are the components of transport system in highly organised plants?
Answer : the main components of the transport system in highly organised plans are (i) xylem ant (ii) phloem.
(I) xylem: it helps to carry water and Minerals obtained from soil to the leaves.
(ii) phloem: it has to transport food prepared by photosynthesis from leaves to various parts of the plants.
Question 4: How are water and Minerals transported in plants?
Answer. Inland water and Minerals transported by xylem. Vessels and tracheids in xylem tissue of root stem and leaves are interconnected to form the continuous water conducting network of tubes reaching all parts of plant. The cells of root which are in contact of soil actively take up ion. As a result, concentration differentiate between cells of root and soil water. therefore there is a study movement of water into xylem by the process of osmosis. show an osmotic pressure is formed and water and Minerals are transported from one cell to the other due to osmosis. On other hand, plant continuously lose water by the process of transpiration. As a result, transpiration pull create which helps to apply of water through xylem to reach the leaves.
Question 5. How is food transported in plants?
Answer. The food is prepared by plant is transported by phloem tissue
The flame tissue consists of sieve tubes along with they are compenion cells. The mechanism of movement of food in phloem by utilising is described as:
The sugar which is made by plant in leaves is transported into the Sheep tubes of phloem using energy from ATP. Then Water enters into sleep tubes which already contain sugar by the process of osmosis due to which the pressure in the phloem tissue Rises. this high pressure produced in the phloem tissue moves the food to all parts of the plant having less pressure in their tissues. By this way phloem transport food according to the needs of the plant.
NCERT chapter life processes page 112
Question 1 : Describe the structure and functioning of neurones.
Answer:
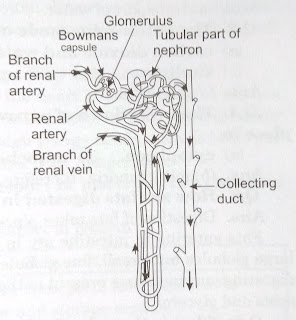
Structure of nephron: nephron is the structural and functional unit of kidney. It is a long coiled tubule, whose one end is com shaped called Bowman capsule and other end connected to a urine collecting duct. Bowman's capsule contains a bundle of blood capillaries known as glomerulus that is followed by the Tubular part of nephron, which forms looks at some places.
Function of nephron:
(a) glomerulus accessor filter which filter the blood passing through it.
(b) glomerulus also removed harmful substances from the body that include nitrogen used materials.
(c) some substances like K+are actively secreted into the urine through the tubule.
(d) the useful substances like glucose , amino acids, salts and a major amount of water is selectively reabsorbed by the Tubular part of nephron.
(e) the collecting duct collects the urine and passes it to the ureter.
Question 2: What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products?
Answer : (I) plants get rid of gaseous waste products through stomata on leaves and lenticels in stems.
(ii) plants get rid of excess water by transpiration.
(iii) plants excrete some west substances into the soil around them.
(IV) plants get rid of west by secreting them in the form of gums and resins.
Question 3: How is the amount of urine produced regulated?
Answer: the amount of urine produced is regulated by reabsorption of water and some of the desert substances into the blood through blood capillaries surrounding the tubules of nephrons. The amount of urine produce d depends on how much excess water is present in the body and how much of desert which are to be excreted.
Exercises
Question 1. the kidney in human beings are a part of the system for
(a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion (IV) transportation.
Answer: excretion
Question 2: the xylem in plants are responsible for (I) transport of water. (ii) transport of food. (iii) transport in amino acids. (IV) transport of oxygen.
Answer: transport of water.
Question 3: the autotrophic mode of nutrition required
(I) carbon dioxide and water. (ii) chlorophyll. (iii) sunlight (IV) all of these.
Answer: all of these
Question 4: The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in
(I) cytoplasm. (ii) mitochondria. (Iii) chloroplast. (IV) nucleus
Answer: mitochondria
NCERT page 95
Question 1. why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans?
Answer: multicellular organisms have to perform many activities for which large amount of energy required. show large amount of food needed to be breaks down which requires large amount of oxygen. But in diffusion process we get very small amount of oxygen which is insufficient for production of large amount of energy.
Question 2. What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive?
Answer: movement growth and respiration are necessary to identify whether something is alive.
Question 3. What are the outside raw materials used by an organism?
Answer. Nutrients water and oxygen are the raw materials obtained from outside.
Question 4. What processes would you consider essential for maintaining life?
Answer. The officers like nutrition respiration transportation excretion reproduction are essential for maintaining life.
NCERT text page 101
Question 1. What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition?
Answer
Question 2. where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
Answer. Water is absorbed by the roots from the soil.
Carbon dioxide is obtained from here through stomata.
Light is obtained from Sun.
Aadhar minerals like Iron Phosphorus magnesium Sulphur and nitrogen collected from the soil by the roots.
Question 3. What is the role of acid in our stomach?
Answer. The hydrochloric acid present in stomach creates an acidic medium which facilitates the action of enzyme pepsin. It kills the germs present in the food.
Question 4 what is the function of digestive enzymes?
Answer. digestive enzymes are the biological catalyst who's break down the complex food molecules into such small particles which can be absorbed from the alimentary canal into the blood stream..
Question 5. How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food?
Answer. The main reason for the absorption of digested food in digestive system is small intestine. The inner lining of small intestine is covered by Mini tiny finger like projections called villi. The presence of Villi gives the inner walls of the small intestine a very large surface area for absorption of digested food.
NCERT book solution page 115
Question 1 what advantages over an aquatic organism does a Terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Answer. The aquatic organisms use the oxygen dissolved in water for carrying out respiration
the amount of oxygen dissolved in water is limited. show the aquatic organisms have a much faster rate of breathing.
Terrestrial organisms take oxygen from atmosphere through respiratory organs. So, they have a much slower breathing rate than aquatic organism.
Question 2. what are the different ways in which glucose is oxidised to provide energy in various organisms?
Answer. Breaking down of glucose takes place in cytoplasm of the cell of all organisms. In this process three carbon molecule compound called pyruvate is produced.
Breaking down of glucose text place in various ways:
(I) anaerobic it is a process in which food is oxidized incompletely in absence of oxygen. For example, an aerobic respiration occur in skeletal muscles when we work hard for long time. During this process carbon dioxide, lactic acid ant energy is produced by the partial breakdown of glucose.
Aerobic respiration: it is the process in which food is completely oxidized in presence of oxygen and form large amount of energy along with carbon dioxide and water
Question 3. How is Oxygen and Carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
Answer : In human beings, oxygen is transported from lungs by the respiratory pigment called hemoglobin which is present in RBC that is red blood corpuscles. Haemoglobin has a very high affinity for oxygen. Carbon dioxide is more soluble in water than oxygen., most of carbon dioxide produced during respiration in the human body is transported in the dissolved form in our blood.
Question 4 how are the lungs designed in human beings to maximize the area for the exchange of gases?
Answer: in human lungs, there are millions of alveoli present. the president of millions of alveoli in lungs increases the surface area of absorption to greater extent. As a result exchange of gases takes place more.
NCERT chapter life process page 110
Question 1. What are the components of transport system in human beings? What are the functions of these components?
Answer. Human transport system consist of heart blood and blood vessels.
Function
(I) heart: it acts as a pumping organ to push and pull blood around the body. It receives the deoxygenated blood from various parts of the body and palms oxygenated blood throughout the body.
(ii) blood: it is a liquid connective tissue. It consists of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma.
Red blood cells: it helps in transportation of nutrients excretory materials hormones gases etc. oxygen is transported as oxyhaemoglobin and carbon dioxide as carbamino hemoglobin.
White blood cells: IIT fight against foreign bodies by producing antibodies and histamine.
Blood platelets: eat play an important role in coagulation of blood.
Blood vessel: blood vessels are a network of vessels. they help in the circulation of blood throughout the body.
Question 2: why it is necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds?
Answer. the mammals and birds are warm blooded animals which have high energy needs because they constantly require energy to maintain their body temperature. it is necessary to separate oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds because such a separation allows a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body cells which is required for producing a lot of energy needed by them.
Question 3. What are the components of transport system in highly organised plants?
Answer : the main components of the transport system in highly organised plans are (i) xylem ant (ii) phloem.
(I) xylem: it helps to carry water and Minerals obtained from soil to the leaves.
(ii) phloem: it has to transport food prepared by photosynthesis from leaves to various parts of the plants.
Question 4: How are water and Minerals transported in plants?
Answer. Inland water and Minerals transported by xylem. Vessels and tracheids in xylem tissue of root stem and leaves are interconnected to form the continuous water conducting network of tubes reaching all parts of plant. The cells of root which are in contact of soil actively take up ion. As a result, concentration differentiate between cells of root and soil water. therefore there is a study movement of water into xylem by the process of osmosis. show an osmotic pressure is formed and water and Minerals are transported from one cell to the other due to osmosis. On other hand, plant continuously lose water by the process of transpiration. As a result, transpiration pull create which helps to apply of water through xylem to reach the leaves.
Question 5. How is food transported in plants?
Answer. The food is prepared by plant is transported by phloem tissue
The flame tissue consists of sieve tubes along with they are compenion cells. The mechanism of movement of food in phloem by utilising is described as:
The sugar which is made by plant in leaves is transported into the Sheep tubes of phloem using energy from ATP. Then Water enters into sleep tubes which already contain sugar by the process of osmosis due to which the pressure in the phloem tissue Rises. this high pressure produced in the phloem tissue moves the food to all parts of the plant having less pressure in their tissues. By this way phloem transport food according to the needs of the plant.
NCERT chapter life processes page 112
Question 1 : Describe the structure and functioning of neurones.
Answer:
Structure of nephron: nephron is the structural and functional unit of kidney. It is a long coiled tubule, whose one end is com shaped called Bowman capsule and other end connected to a urine collecting duct. Bowman's capsule contains a bundle of blood capillaries known as glomerulus that is followed by the Tubular part of nephron, which forms looks at some places.
Function of nephron:
(a) glomerulus accessor filter which filter the blood passing through it.
(b) glomerulus also removed harmful substances from the body that include nitrogen used materials.
(c) some substances like K+are actively secreted into the urine through the tubule.
(d) the useful substances like glucose , amino acids, salts and a major amount of water is selectively reabsorbed by the Tubular part of nephron.
(e) the collecting duct collects the urine and passes it to the ureter.
Question 2: What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products?
Answer : (I) plants get rid of gaseous waste products through stomata on leaves and lenticels in stems.
(ii) plants get rid of excess water by transpiration.
(iii) plants excrete some west substances into the soil around them.
(IV) plants get rid of west by secreting them in the form of gums and resins.
Question 3: How is the amount of urine produced regulated?
Answer: the amount of urine produced is regulated by reabsorption of water and some of the desert substances into the blood through blood capillaries surrounding the tubules of nephrons. The amount of urine produce d depends on how much excess water is present in the body and how much of desert which are to be excreted.
Exercises
Question 1. the kidney in human beings are a part of the system for
(a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion (IV) transportation.
Answer: excretion
Question 2: the xylem in plants are responsible for (I) transport of water. (ii) transport of food. (iii) transport in amino acids. (IV) transport of oxygen.
Answer: transport of water.
Question 3: the autotrophic mode of nutrition required
(I) carbon dioxide and water. (ii) chlorophyll. (iii) sunlight (IV) all of these.
Answer: all of these
Question 4: The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in
(I) cytoplasm. (ii) mitochondria. (Iii) chloroplast. (IV) nucleus
Answer: mitochondria
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes with answers
You May Also Like
You May Also Like
2. NCERT solutions Carbon and its Compounds
3. NCERT solutions Periodic Classification of Elements